Nonlinear Analysis Seminar
Topics discussed
The seminar is devoted to discussing problems in nonlinear analysis. Instead of presenting known results, we prefer to discuss open problems connected with the current research of the seminar members.
We pay particular attention to the following topics:
1. Fixed point theorems for various classes of mappings acting in linear vector spaces, hyperconvex metric spaces or absolute retracts.
2. Almost periodic and almost automorphic functions and their generalizations, and applications to differential and integral equations.
3. Functions of bounded variation with applications to the theory of nonlinear integral and superposition operators.
4. Existence and uniqueness of solutions to nonlinear integral equations in spaces of functions of bounded variation (in various senses).
5. Existence and topological structure of solutions sets of nonlinear differential and integral equations in finite-dimensional and abstract spaces.
6. Selected topics from general topology: measures of noncompactness, hyperconvex spaces, R-trees and others.
7. Selected topics in the theory of nonabsolute convergent integrals.
8. Selected problems of formal analysis.
Seminar dates
Seminars are held on Tuesdays at 10:45am in room B3-38 of Collegium Mathematicum at Uniwersytetu Poznańskiego 4 in Poznań.
21-05-2024 | Piotr Maćkowiak: The Riordan group, part 7
During the seminar there will be presented basic notions associated with the Riordan group. The lecture is based on:
- G.-S. Cheon, H. Kim, L.W. Shapiro,Riordan group involutions, Linear Algebra and its Applications 428, 2008, 941-952.
- X.-X. Gan, Formal analysis. An introduction, De Gruyter, 2021.
- L. W. Shapiro, S. Getu, W.-J. Woan, L. Woodson, The Riordan group, Discrete Appl. Math. 34, 1991, 229-239.
- L. Shapiro et al., The Riordan Group and Applications, Springer, 2022.
14-05-2024 | Piotr Maćkowiak: The Riordan group, part 6
During the seminar there will be presented basic notions associated with the Riordan group. The lecture is based on:
- G.-S. Cheon, H. Kim, L.W. Shapiro,Riordan group involutions, Linear Algebra and its Applications 428, 2008, 941-952.
- X.-X. Gan, Formal analysis. An introduction, De Gruyter, 2021.
- L. W. Shapiro, S. Getu, W.-J. Woan, L. Woodson, The Riordan group, Discrete Appl. Math. 34, 1991, 229-239.
- L. Shapiro et al., The Riordan Group and Applications, Springer, 2022.
07-05-2024 | Piotr Kasprzak: Universal meaure of non-conpactaness
23-04-2024 | Adam Nawrocki: The convolution of Besicovitch almost periodic functions with integrable functions, part 6
The aim of the seminar is to verify the following results regarding the convolution.
For a Besicovitch almost periodic function (\(B^p\)-a.p.) \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that \(t\cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) the convolution \(f*g\) exists almost everywhere and it is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover
\(||f*g||_{B}\leq ||f||_{B}\cdot ||g||_{L^1(\mathbb R)},\) where \( ||f||_B=\limsup_{T \to \infty}\frac{1}{2T}\int_{-T}^T f(t)dt.\)
We consider the case \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) and \(t\cdot g(t) \notin L^1(\mathbb R)\). We will give an example of \(B^p\)-a.p. \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that the convolution \(f*g\) does not exist. Next, we will give an example of functions \(f, g\) such that
\(||f||_B=0, g \in L^1(\mathbb R), \forall_{ \alpha \in (0,1)} \quad |t|^{\alpha} \cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) for which the convolution \(f*g\) exists and \(||f*g||_B=+\infty\).
During the seminar, we will indicate a certain class of \(B^p\)-a.p. functions for which the following property holds
If for some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) we have \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) (at \(\pm \infty\)) and for some \(\alpha<\beta<1\) we have \(|g(t)|=O(|t|^{-1-\beta})\) (w \(\pm \infty\)), then the convolution \(f*g\) exists for all \(t \in \mathbb R\) and it is \(B^p\)-a.p.
An example of a \(B^p\)-a.p. function that satisfies the asymptotic properties \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) by some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) is dzeta Riemann function \(\zeta\). It is known in the literature that in the area \(\{s\in \mathbb C \colon \frac{1}{2}<\Re (s)<1 \}\) the function
\(t \to \zeta(\sigma +it),\) \((\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1)\)
is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover for each \(\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1\) and \(\varepsilon>0\) we have the following estimation
\(|\zeta(\sigma +it)|=O(|t|^{\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2}\sigma+\varepsilon}).\)09-04-2024 | Katarzyna Krzywdzińska-Rybarczyk: Catalan numbers
The aim of the seminar is to discuss a few types of random walks on lattices and to show that the number of such walks of certain length is closely connected with Catalan numbers.
26-03-2024 | Adam Nawrocki: The convolution of Besicovitch almost periodic functions with integrable functions, part 5
The aim of the seminar is to verify the following results regarding the convolution.
For a Besicovitch almost periodic function (\(B^p\)-a.p.) \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that \(t\cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) the convolution \(f*g\) exists almost everywhere and it is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover
\(||f*g||_{B}\leq ||f||_{B}\cdot ||g||_{L^1(\mathbb R)},\) where \( ||f||_B=\limsup_{T \to \infty}\frac{1}{2T}\int_{-T}^T f(t)dt.\)
We consider the case \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) and \(t\cdot g(t) \notin L^1(\mathbb R)\). We will give an example of \(B^p\)-a.p. \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that the convolution \(f*g\) does not exist. Next, we will give an example of functions \(f, g\) such that
\(||f||_B=0, g \in L^1(\mathbb R), \forall_{ \alpha \in (0,1)} \quad |t|^{\alpha} \cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) for which the convolution \(f*g\) exists and \(||f*g||_B=+\infty\).
During the seminar, we will indicate a certain class of \(B^p\)-a.p. functions for which the following property holds
If for some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) we have \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) (at \(\pm \infty\)) and for some \(\alpha<\beta<1\) we have \(|g(t)|=O(|t|^{-1-\beta})\) (w \(\pm \infty\)), then the convolution \(f*g\) exists for all \(t \in \mathbb R\) and it is \(B^p\)-a.p.
An example of a \(B^p\)-a.p. function that satisfies the asymptotic properties \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) by some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) is dzeta Riemann function \(\zeta\). It is known in the literature that in the area \(\{s\in \mathbb C \colon \frac{1}{2}<\Re (s)<1 \}\) the function
\(t \to \zeta(\sigma +it),\) \((\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1)\)
is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover for each \(\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1\) and \(\varepsilon>0\) we have the following estimation
\(|\zeta(\sigma +it)|=O(|t|^{\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2}\sigma+\varepsilon}).\)12-03-2024 | Adam Nawrocki: The convolution of Besicovitch almost periodic functions with integrable functions, part 4
The aim of the seminar is to verify the following results regarding the convolution.
For a Besicovitch almost periodic function (\(B^p\)-a.p.) \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that \(t\cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) the convolution \(f*g\) exists almost everywhere and it is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover
\(||f*g||_{B}\leq ||f||_{B}\cdot ||g||_{L^1(\mathbb R)},\) where \( ||f||_B=\limsup_{T \to \infty}\frac{1}{2T}\int_{-T}^T f(t)dt.\)
We consider the case \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) and \(t\cdot g(t) \notin L^1(\mathbb R)\). We will give an example of \(B^p\)-a.p. \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that the convolution \(f*g\) does not exist. Next, we will give an example of functions \(f, g\) such that
\(||f||_B=0, g \in L^1(\mathbb R), \forall_{ \alpha \in (0,1)} \quad |t|^{\alpha} \cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) for which the convolution \(f*g\) exists and \(||f*g||_B=+\infty\).
During the seminar, we will indicate a certain class of \(B^p\)-a.p. functions for which the following property holds
If for some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) we have \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) (at \(\pm \infty\)) and for some \(\alpha<\beta<1\) we have \(|g(t)|=O(|t|^{-1-\beta})\) (w \(\pm \infty\)), then the convolution \(f*g\) exists for all \(t \in \mathbb R\) and it is \(B^p\)-a.p.
An example of a \(B^p\)-a.p. function that satisfies the asymptotic properties \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) by some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) is dzeta Riemann function \(\zeta\). It is known in the literature that in the area \(\{s\in \mathbb C \colon \frac{1}{2}<\Re (s)<1 \}\) the function
\(t \to \zeta(\sigma +it),\) \((\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1)\)
is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover for each \(\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1\) and \(\varepsilon>0\) we have the following estimation
\(|\zeta(\sigma +it)|=O(|t|^{\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2}\sigma+\varepsilon}).\)27-02-2024 | Adam Nawrocki: The convolution of Besicovitch almost periodic functions with integrable functions, part 3
The aim of the seminar is to verify the following results regarding the convolution.
For a Besicovitch almost periodic function (\(B^p\)-a.p.) \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that \(t\cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) the convolution \(f*g\) exists almost everywhere and it is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover
\(||f*g||_{B}\leq ||f||_{B}\cdot ||g||_{L^1(\mathbb R)},\) where \( ||f||_B=\limsup_{T \to \infty}\frac{1}{2T}\int_{-T}^T f(t)dt.\)
We consider the case \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) and \(t\cdot g(t) \notin L^1(\mathbb R)\). We will give an example of \(B^p\)-a.p. \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that the convolution \(f*g\) does not exist. Next, we will give an example of functions \(f, g\) such that
\(||f||_B=0, g \in L^1(\mathbb R), \forall_{ \alpha \in (0,1)} \quad |t|^{\alpha} \cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) for which the convolution \(f*g\) exists and \(||f*g||_B=+\infty\).
During the seminar, we will indicate a certain class of \(B^p\)-a.p. functions for which the following property holds
If for some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) we have \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) (at \(\pm \infty\)) and for some \(\alpha<\beta<1\) we have \(|g(t)|=O(|t|^{-1-\beta})\) (w \(\pm \infty\)), then the convolution \(f*g\) exists for all \(t \in \mathbb R\) and it is \(B^p\)-a.p.
An example of a \(B^p\)-a.p. function that satisfies the asymptotic properties \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) by some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) is dzeta Riemann function \(\zeta\). It is known in the literature that in the area \(\{s\in \mathbb C \colon \frac{1}{2}<\Re (s)<1 \}\) the function
\(t \to \zeta(\sigma +it),\) \((\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1)\)
is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover for each \(\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1\) and \(\varepsilon>0\) we have the following estimation
\(|\zeta(\sigma +it)|=O(|t|^{\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2}\sigma+\varepsilon}).\)23-01-2024 | Motaz Mokatren: Multivariable Riordan matrices, part 4
We construct a Riordan matrix of formal power series in several variables, which we will recall a multi variable Riordan matrix. We show that such matrices form a group structure and provide some properties regarding such matrices.
09-01-2024 | Motaz Mokatren: Multivariable Riordan matrices, part 3
We construct a Riordan matrix of formal power series in several variables, which we will recall a multi variable Riordan matrix. We show that such matrices form a group structure and provide some properties regarding such matrices.
19-12-2023 | Motaz Mokatren: Multivariable Riordan matrices, part 2
We construct a Riordan matrix of formal power series in several variables, which we will recall a multi variable Riordan matrix. We show that such matrices form a group structure and provide some properties regarding such matrices.
12-12-2023 | Motaz Mokatren: Multivariable Riordan matrices, part 1
We construct a Riordan matrix of formal power series in several variables, which we will recall a multi variable Riordan matrix. We show that such matrices form a group structure and provide some properties regarding such matrices.
28-11-2023 | Adam Nawrocki: The convolution of Besicovitch almost periodic functions with integrable functions, part 2
The aim of the seminar is to verify the following results regarding the convolution.
For a Besicovitch almost periodic function (\(B^p\)-a.p.) \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that \(t\cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) the convolution \(f*g\) exists almost everywhere and it is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover
\(||f*g||_{B}\leq ||f||_{B}\cdot ||g||_{L^1(\mathbb R)},\) where \( ||f||_B=\limsup_{T \to \infty}\frac{1}{2T}\int_{-T}^T f(t)dt.\)
We consider the case \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) and \(t\cdot g(t) \notin L^1(\mathbb R)\). We will give an example of \(B^p\)-a.p. \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that the convolution \(f*g\) does not exist. Next, we will give an example of functions \(f, g\) such that
\(||f||_B=0, g \in L^1(\mathbb R), \forall_{ \alpha \in (0,1)} \quad |t|^{\alpha} \cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) for which the convolution \(f*g\) exists and \(||f*g||_B=+\infty\).
During the seminar, we will indicate a certain class of \(B^p\)-a.p. functions for which the following property holds
If for some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) we have \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) (at \(\pm \infty\)) and for some \(\alpha<\beta<1\) we have \(|g(t)|=O(|t|^{-1-\beta})\) (w \(\pm \infty\)), then the convolution \(f*g\) exists for all \(t \in \mathbb R\) and it is \(B^p\)-a.p.
An example of a \(B^p\)-a.p. function that satisfies the asymptotic properties \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) by some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) is dzeta Riemann function \(\zeta\). It is known in the literature that in the area \(\{s\in \mathbb C \colon \frac{1}{2}<\Re (s)<1 \}\) the function
\(t \to \zeta(\sigma +it),\) \((\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1)\)
is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover for each \(\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1\) and \(\varepsilon>0\) we have the following estimation
\(|\zeta(\sigma +it)|=O(|t|^{\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2}\sigma+\varepsilon}).\)21-11-2023 | Adam Nawrocki: The convolution of Besicovitch almost periodic functions with integrable functions, part 1
The aim of the seminar is to verify the following results regarding the convolution.
For a Besicovitch almost periodic function (\(B^p\)-a.p.) \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that \(t\cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) the convolution \(f*g\) exists almost everywhere and it is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover
\(||f*g||_{B}\leq ||f||_{B}\cdot ||g||_{L^1(\mathbb R)},\) where \( ||f||_B=\limsup_{T \to \infty}\frac{1}{2T}\int_{-T}^T f(t)dt.\)
We consider the case \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) and \(t\cdot g(t) \notin L^1(\mathbb R)\). We will give an example of \(B^p\)-a.p. \(f\) and \(g \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) such that the convolution \(f*g\) does not exist. Next, we will give an example of functions \(f, g\) such that
\(||f||_B=0, g \in L^1(\mathbb R), \forall_{ \alpha \in (0,1)} \quad |t|^{\alpha} \cdot g(t) \in L^1(\mathbb R)\) for which the convolution \(f*g\) exists and \(||f*g||_B=+\infty\).
During the seminar, we will indicate a certain class of \(B^p\)-a.p. functions for which the following property holds
If for some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) we have \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) (at \(\pm \infty\)) and for some \(\alpha<\beta<1\) we have \(|g(t)|=O(|t|^{-1-\beta})\) (w \(\pm \infty\)), then the convolution \(f*g\) exists for all \(t \in \mathbb R\) and it is \(B^p\)-a.p.
An example of a \(B^p\)-a.p. function that satisfies the asymptotic properties \(|f(t)|=O (|t|^{\alpha})\) by some \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\) is dzeta Riemann function \(\zeta\). It is known in the literature that in the area \(\{s\in \mathbb C \colon \frac{1}{2}<\Re (s)<1 \}\) the function
\(t \to \zeta(\sigma +it),\) \((\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1)\)
is \(B^p\)-a.p. Moreover for each \(\frac{1}{2}<\sigma<1\) and \(\varepsilon>0\) we have the following estimation
\(|\zeta(\sigma +it)|=O(|t|^{\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2}\sigma+\varepsilon}).\)14-11-2023 | Piotr Maćkowiak: The Riordan group, part 5
During the seminar there will be presented basic notions associated with the Riordan group. The lecture is based on:
- G.-S. Cheon, H. Kim, L.W. Shapiro,Riordan group involutions, Linear Algebra and its Applications 428, 2008, 941-952.
- X.-X. Gan, Formal analysis. An introduction, De Gruyter, 2021.
- L. W. Shapiro, S. Getu, W.-J. Woan, L. Woodson, The Riordan group, Discrete Appl. Math. 34, 1991, 229-239.
- L. Shapiro et al., The Riordan Group and Applications, Springer, 2022.
07-11-2023 | Piotr Maćkowiak: The Riordan group, part 4
During the seminar there will be presented basic notions associated with the Riordan group. The lecture is based on:
- G.-S. Cheon, H. Kim, L.W. Shapiro,Riordan group involutions, Linear Algebra and its Applications 428, 2008, 941-952.
- X.-X. Gan, Formal analysis. An introduction, De Gruyter, 2021.
- L. W. Shapiro, S. Getu, W.-J. Woan, L. Woodson, The Riordan group, Discrete Appl. Math. 34, 1991, 229-239.
- L. Shapiro et al., The Riordan Group and Applications, Springer, 2022.
31-10-2023 | Piotr Maćkowiak: The Riordan group, part 3
During the seminar there will be presented basic notions associated with the Riordan group. The lecture is based on:
- G.-S. Cheon, H. Kim, L.W. Shapiro,Riordan group involutions, Linear Algebra and its Applications 428, 2008, 941-952.
- X.-X. Gan, Formal analysis. An introduction, De Gruyter, 2021.
- L. W. Shapiro, S. Getu, W.-J. Woan, L. Woodson, The Riordan group, Discrete Appl. Math. 34, 1991, 229-239.
- L. Shapiro et al., The Riordan Group and Applications, Springer, 2022.
24-10-2023 | Piotr Maćkowiak: The Riordan group, part 2
During the seminar there will be presented basic notions associated with the Riordan group. The lecture is based on:
- G.-S. Cheon, H. Kim, L.W. Shapiro,Riordan group involutions, Linear Algebra and its Applications 428, 2008, 941-952.
- X.-X. Gan, Formal analysis. An introduction, De Gruyter, 2021.
- L. W. Shapiro, S. Getu, W.-J. Woan, L. Woodson, The Riordan group, Discrete Appl. Math. 34, 1991, 229-239.
- L. Shapiro et al., The Riordan Group and Applications, Springer, 2022.
17-10-2023 | Piotr Maćkowiak: The Riordan group, part 1
During the seminar there will be presented basic notions associated with the Riordan group. The lecture is based on:
- G.-S. Cheon, H. Kim, L.W. Shapiro,Riordan group involutions, Linear Algebra and its Applications 428, 2008, 941-952.
- X.-X. Gan, Formal analysis. An introduction, De Gruyter, 2021.
- L. W. Shapiro, S. Getu, W.-J. Woan, L. Woodson, The Riordan group, Discrete Appl. Math. 34, 1991, 229-239.
- L. Shapiro et al., The Riordan Group and Applications, Springer, 2022.
30-05-2022 | Adam Nawrocki: Fibonacci Quasicrystal, part 4
In the theory of quasicrystals, the classic example of an aperiodic structure is the so-called Fibonacci chain also known as the Fibonacci word. Using the theory of Combinatorics on Words we will give an arithmetic description of this object. Then we will prove that the Fibonacci word is a mathematical quasicrystal. We will also get to know examples of other structures with similar properties.
09-05-2023 | Jacek Gulgowski: \(\phi\)-Hoelder functions for nonconcave \(\phi\)
One of the simple (but important) results from the basic course of Mathematical Analysis is the observation that every Hoelder continuous function with the exponent bigger then 1 is necessarily a constant. This naturally works for functions defined on open and connected domains of euclidean space. But, when considering more complex domain, we may find examples of nontrivial Hoelder continuous fnctions with exponent bigger than 1 – the examples of such situations are known since decades. We will focus on the very interesting construction, which for any function \(\phi\) (no matter how quickly approaching 0) gives the compact domain (a subset of a Hilbert space) and a function which satisfies Hoelder condition for a function \(\phi\). The talk is based on the paper Besicovitch, Schoenberg, On Jordan arcs and Lipchitz classes of functions defined by them, Acta Mathematica 106 (1961), 113–136.
25-04-2023 | Marek Kapera: Learning own preferences through consumption, part 2
This study provides theoretical foundations for preference discovery theory. We propose to relax the assumption that the consumer has perfect knowledge of their own preferences, so that the consumer knows only the subjective probability of those alternatives being in any given relation, which is conditional on the information available to the consumer. To achieve that, we construct probabilistic measures on the space of all permissible preference relations and consider the consumer to be equipped with one such measure, instead of a preference relation. These measures are intrinsically linked by construction to the information structure available to the consumer and allow for indirect learning. We visualize how these measures correspond to the choices of the consumer, we consider three distinct decision procedures. These procedures formalize how under different assumptions regarding the underlying probability measure, the consumer guesses their own tastes. Finally, we use these measures to define the value of the information provided by the consumption of a chosen alternative and study the properties of the preference ranking induced by it.
04-04-2023 | Marek Kapera: Learning own preferences through consumption, part 1
This study provides theoretical foundations for preference discovery theory. We propose to relax the assumption that the consumer has perfect knowledge of their own preferences, so that the consumer knows only the subjective probability of those alternatives being in any given relation, which is conditional on the information available to the consumer. To achieve that, we construct probabilistic measures on the space of all permissible preference relations and consider the consumer to be equipped with one such measure, instead of a preference relation. These measures are intrinsically linked by construction to the information structure available to the consumer and allow for indirect learning. We visualize how these measures correspond to the choices of the consumer, we consider three distinct decision procedures. These procedures formalize how under different assumptions regarding the underlying probability measure, the consumer guesses their own tastes. Finally, we use these measures to define the value of the information provided by the consumption of a chosen alternative and study the properties of the preference ranking induced by it.
21-03-2023 | Jerzy Grzybowski: On maximal Demyanov’s difference and Minkowski sum with maximal number of vertices, part 2
Demyanov’s difference of compact convex sets is related to Clarke subdifferential of nondifferentiable function. We investigate when this difference of sets A and B is equal to Minkowski sum A+(-B). The problem is related to Minkowski sum of polytopes A+B with maximal number of vertexes. We present some criteria and examples of such polytopes.
07-03-2023 | Jerzy Grzybowski: On maximal Demyanov’s difference and Minkowski sum with maximal number of vertices, part 1
Demyanov’s difference of compact convex sets is related to Clarke subdifferential of nondifferentiable function. We investigate when this difference of sets A and B is equal to Minkowski sum A+(-B). The problem is related to Minkowski sum of polytopes A+B with maximal number of vertexes. We present some criteria and examples of such polytopes.
31-01-2023 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Formal power series in several variables, part 4
During the seminar we will present basics of the theory of formal power series in several variables and some applications of that theory. The talk is based on the paper P. Haukkanen, Formal power series in several variables, Notes on Number Theory and Discrete Mathematics, vol. 25, 2019.
17-01-2023 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Formal power series in several variables, part 3
During the seminar we will present basics of the theory of formal power series in several variables and some applications of that theory. The talk is based on the paper P. Haukkanen, Formal power series in several variables, Notes on Number Theory and Discrete Mathematics, vol. 25, 2019.
10-01-2023 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Formal power series in several variables, part 2
During the seminar we will present basics of the theory of formal power series in several variables and some applications of that theory. The talk is based on the paper P. Haukkanen, Formal power series in several variables, Notes on Number Theory and Discrete Mathematics, vol. 25, 2019.
03-01-2023 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Formal power series in several variables, part 1
During the seminar we will present basics of the theory of formal power series in several variables and some applications of that theory. The talk is based on the paper P. Haukkanen, Formal power series in several variables, Notes on Number Theory and Discrete Mathematics, vol. 25, 2019.
13-12-2022 | Jacek Gulgowski: Operators with nonsingular kernel in fractional order calculus
There are many different definitions of fractional order derivatives. Quite recently some of these, which correspond to the integral operators with nonsingular kernel, appeared. It may be observed that these operators are actually not different than the integral order differential operators. The presentation is insipred by the paper “Why fractional derivatives with nonsingular kernels should not be used“, Kai Diethelm , Roberto Garrappa , Andrea Giusti and Martin Stynes, Journal of Fractional Calculus and Applied Analysis, 2020.
29-11-2022 | Jacek Gulgowski: Compactness in the spaces of functions of bounded variation
Quite recently, the paper with compactness criteria for different spaces of Banach-space valued functions of bounded variation appeared (cf. Y. Si, J. Xu, Relatively compact sets of Banach space-valued bounded-variation spaces, Banach J. Math. Anal. 17 (2023), no. 7). I would like to compare these results to the research conducted in our team.
15-11-2022 | Jacek Gulgowski: Paths of bounded variation in machine learning
The time series analysis is often related to the classification of the series of data or to the prediction how the data series is going to evolve. Both applications may be perceived as the operation, which assigns a number, or an element of the appropriate linear space, to a sequence of data (it is sometimes referred to as “the labelling problem”). The time series may be understood as the trajectories of some stochastic process. If we assume that the trajectories are functions of bounded variation, then it may be proved that the values of any (reasonable) function defined on a compact set of admissible trajectories may be approximated by some linear functional of the, so called, signature of a trajectory. The presentation is inspired by a preprint”Optimal Estimation of Generic Dynamics by Path-Dependent Neural Jump ODEs”, Florian Krach, Marc Nübel, Josef Teichmann (arXiv:2206.14284)
08-11-2022 | Adam Nawrocki: Fibonacci Quasicrystal, part 3
In the theory of quasicrystals, the classic example of an aperiodic structure is the so-called Fibonacci chain also known as the Fibonacci word. Using the theory of Combinatorics on Words we will give an arithmetic description of this object. Then we will prove that the Fibonacci word is a mathematical quasicrystal. We will also get to know examples of other structures with similar properties.
25-10-2022 | Adam Nawrocki: Fibonacci Quasicrystal, part 2
In the theory of quasicrystals, the classic example of an aperiodic structure is the so-called Fibonacci chain also known as the Fibonacci word. Using the theory of Combinatorics on Words we will give an arithmetic description of this object. Then we will prove that the Fibonacci word is a mathematical quasicrystal. We will also get to know examples of other structures with similar properties.
11-10-2022 | Adam Nawrocki: Fibonacci Quasicrystal, part 1
In the theory of quasicrystals, the classic example of an aperiodic structure is the so-called Fibonacci chain also known as the Fibonacci word. Using the theory of Combinatorics on Words we will give an arithmetic description of this object. Then we will prove that the Fibonacci word is a mathematical quasicrystal. We will also get to know examples of other structures with similar properties.
14-06-2022 | Piotr Kasprzak: Compactness crietria in some function spaces, part 3
Compactness criteria are one of the main tools of nonlinear analysis used to study compactness properties of certain operators or embeddings of spaces. During the seminar we will present several – classical as well as completely new – compactness criteria in some function spaces. The proofs of the new results will be based on a recently introduced notion of a equinormed set.
31-05-2022 | Piotr Kasprzak: Compactness crietria in some function spaces, part 2
Compactness criteria are one of the main tools of nonlinear analysis used to study compactness properties of certain operators or embeddings of spaces. During the seminar we will present several – classical as well as completely new – compactness criteria in some function spaces. The proofs of the new results will be based on a recently introduced notion of a equinormed set.
17-05-2022 | Piotr Kasprzak: Compactness crietria in some function spaces, part 1
Compactness criteria are one of the main tools of nonlinear analysis used to study compactness properties of certain operators or embeddings of spaces. During the seminar we will present several – classical as well as completely new – compactness criteria in some function spaces. The proofs of the new results will be based on a recently introduced notion of a equinormed set.
12-04-2022 | Dawid Bugajewski: Searching for power series solutions to Schrödinger equation with applications, part 2
At the seminar we will present an application of the power series method to the analysis of the Schrödinger equation. We will look for solutions to this equation in the form of uniformly convergent power series of many variables and power series with functional coefficients. The obtained results will be used, inter alia, to study particles with a time-dependent potential energy, particles
trapped in one-dimensional curves or Hilbert spaces of quantum states.
29-03-2022 | Dawid Bugajewski: Searching for power series solutions to Schrödinger equation with applications, part 1
At the seminar we will present an application of the power series method to the analysis of the Schrödinger equation. We will look for solutions to this equation in the form of uniformly convergent power series of many variables and power series with functional coefficients. The obtained results will be used, inter alia, to study particles with a time-dependent potential energy, particles
trapped in one-dimensional curves or Hilbert spaces of quantum states.
15-03-2022 | Jerzy Grzybowski: On certain properties of pairs of convex sets
We present conditions of convexity of a union of each pair of sets belonging to a quotient class of a given pair of sets. We discuss when Demyanov’s difference of two convex sets is equal to their algebraic difference.
08-03-2022 | Jacek Gulgowski: Mathematical methods for evaluation of causality, part 2
The theory of signals and systems identifies causality as a natural property, which is responsible for the fact that the effect does not precede the cause. I am going to describe this concept from the perspective of mathematics and the mathematical tools need to describe it – mostly classical. I will also present their nontrivial applications in studying certain systems induced by differential equations of the fractional order.
01-03-2022 | Jacek Gulgowski: Mathematical methods for evaluation of causality, part 1
The theory of signals and systems identifies causality as a natural property, which is responsible for the fact that the effect does not precede the cause. I am going to describe this concept from the perspective of mathematics and the mathematical tools need to describe it – mostly classical. I will also present their nontrivial applications in studying certain systems induced by differential equations of the fractional order.
01-02-2022 | Wojciech Pałubicki: Wood combustion in 3D
11-01-2022 | Wacław Marzantowicz: Periodic points of maps – a topological approach, part 2
Let \(f\colon X \to X\) be a continuous map of compact closed manifold. A point \(x \in X\) is called a periodic point of \(f\) of period \(n\) if there exists \(n \in \mathbb N\) such that \(f^n(x) = x\). We will present a survey of methods based on the classical Lefschetz and Nielsen theories which estimate (from below) the number periodic points of period \(n\) and describe appearing minimal periods. By their constructions these methods give invariants which are preserved by a homotopy of map. Consequently they are rough but on the other side stable, i.e. these invariants are preserved by a deformation, in particular by a small perturbation of map. A combination of these methods with another assumptions on \(f\) , as \(C^1\)-smoothness, symmetry, analyticity let us to improve essentially results.
04-01-2022 | Wacław Marzantowicz: Periodic points of maps – a topological approach, part 1
Let \(f\colon X \to X\) be a continuous map of compact closed manifold. A point \(x \in X\) is called a periodic point of \(f\) of period \(n\) if there exists \(n \in \mathbb N\) such that \(f^n(x) = x\). We will present a survey of methods based on the classical Lefschetz and Nielsen theories which estimate (from below) the number periodic points of period \(n\) and describe appearing minimal periods. By their constructions these methods give invariants which are preserved by a homotopy of map. Consequently they are rough but on the other side stable, i.e. these invariants are preserved by a deformation, in particular by a small perturbation of map. A combination of these methods with another assumptions on \(f\) , as \(C^1\)-smoothness, symmetry, analyticity let us to improve essentially results.
21-12-2021 | Mariusz Puchalski: Methods of explicitly correlated functions in precise calculations for light atomic and molecular systems – applications
In the second part of the presentation, I will focus on the practical aspects of explicitly correlated function methods and their applications in calculations for atomic and molecular systems. When discussing the developed algorithms and numerical methods using exponential and Gaussian functions, I will pay special attention to limitations and unresolved mathematical problems.
07-12-2021 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Integration of correspondences, part 2
During the seminar, the construction of the integral for correspondences with compact and convex values will be presented. The reading is based on the paper G. Debreu, Integration of correspondences, 5th Berkeley Symposium, 1967.
16-11-2021 | Mariusz Puchalski: Methods of explicitly correlated functions in precise calculations for light atomic and molecular systems
09-11-2021 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Integration of correspondences
During the seminar, the construction of the integral for correspondences with compact and convex values will be presented. The reading is based on the paper G. Debreu, Integration of correspondences, 5th Berkeley Symposium, 1967.
26-10-2021 | Dawid Bugajewski: The inverse and the composition in the set of formal Laurent series, part 2
The goal of this lecture is to discuss the problem of inverse of formal Laurent series. We are going to consider their some non-typical behaviour and try to indicate their causes. We will also discuss the topic of the composition of formal Laurent series along with its properties.
12-10-2021 | Justyna Rychły-Gruszecka : Magnonic crystals and quasicrystals: influence of different types of ordering on spin wave propagation in ferromagnetic materials
Quasicrystals are structures exhibiting long-range ordering with no translational periodicity. A notable symmetry property of quasicrystals is self-similarity by scaling. In this seminar I will present the results of my research concerning the dynamics of spin waves (collective, propagating precessional magnetisation disturbances) in magnonic quasicrystals, which are quasiperiodically structured magnetic materials with element sizes ranging from several tens of nm to micrometres. I will compare results obtained for quasiperiodically and periodically structured magnetic materials (so-called magnonic crystals). I will show that magnonic quasiperiodic crystals provide much wider possibilities of spin wave control compared to regular magnonic crystals. They offer complex, self-similar spin wave spectra, localization of spin waves inside the structure and on its surfaces. Finally, experimental results will be presented, showing the possibility of spin wave propagation through magnonic quasicrystals, the opening of additional frequency gaps, the possibility of reprogramming resonance frequencies depending on the order of magnetisation in quasicrystals.
05-10-2021 | Dawid Bugajewski: The inverse and the composition in the set of formal Laurent series
The goal of this lecture is to discuss the problem of inverse of formal Laurent series. We are going to consider their some non-typical behaviour and try to indicate their causes. We will also discuss the topic of the composition of formal Laurent series along with its properties.
15-06-2021 | Piotr Kasprzak: Some remarks concerning compactness in normed spaces, part 2
During the seminar we are going to discuss some compactness criteria in normed spaces. We will also show how to apply those criteria to obtain classical results in \(l^p\) and \(C(X,\mathbb R)\).
08-06-2021 | Piotr Kasprzak: Some remarks concerning compactness in normed spaces, part 1
During the seminar we are going to discuss some compactness criteria in normed spaces. We will also show how to apply those criteria to obtain classical results in \(l^p\) and \(C(X,\mathbb R)\).
25-05-2021 | Jerzy Gyrzbowski: Pontryagin’s alternating integral and differential games of pursuit, part 2
The differential game arises in the study of the process of the pursuit of one controlled object by another, say airplanes. The aim of the first airplane is to overtake the second, while that of the second is to evade pursuit. To solve this problem, that is, to answer the question whether evasion is possible or not, Pontryagin’s alternating integral (based on the Minkowski sum and the Pontryagin difference of convex sets) is used.
11-05-2021 | Jerzy Gyrzbowski: Pontryagin’s alternating integral and differential games of pursuit, part 1
The differential game arises in the study of the process of the pursuit of one controlled object by another, say airplanes. The aim of the first airplane is to overtake the second, while that of the second is to evade pursuit. To solve this problem, that is, to answer the question whether evasion is possible or not, Pontryagin’s alternating integral (based on the Minkowski sum and the Pontryagin difference of convex sets) is used.
04-05-2021 | Wojciech Dybalski: Mathematical approaches to quantum field theory, part 2
In this talk I will give a non-technical introduction to various mathematical approaches to quantum field theory. These include the Wightman setting based on the theory of operator-valued tempered distributions, the C*-algebraic Haag-Kastler framework and the Osterwalder-Schrader setting relying on measure theory. Relations between different approaches will be discussed.
20-04-2021 | Jacek Gulgowski: Introduction to the least gradient problem in BV spaces, part 2
We are going to present an introduction to the least gradient problem, in a class of functions \(u\in BV(\Omega)\) in open and bounded subsets \(\Omega\subseteq{\mathbb R}^N\), satisfying some additional assumptions and given boundary conditions. The presentation will follow the paper by W. Górny, “(Non)uniqueness of minimizers in the least gradient problem” published in Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 468 (2018), pp. 913-938.
13-04-2021 | Jacek Gulgowski: Introduction to the least gradient problem in BV spaces, part 1
We are going to present an introduction to the least gradient problem, in a class of functions \(u\in BV(\Omega)\) in open and bounded subsets \(\Omega\subseteq{\mathbb R}^N\), satisfying some additional assumptions and given boundary conditions. The presentation will follow the paper by W. Górny, “(Non)uniqueness of minimizers in the least gradient problem” published in Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 468 (2018), pp. 913-938.
30-03-2021 | Wojciech Dybalski: Mathematical approaches to quantum field theory, part 1
In this talk I will give a non-technical introduction to various mathematical approaches to quantum field theory. These include the Wightman setting based on the theory of operator-valued tempered distributions, the C*-algebraic Haag-Kastler framework and the Osterwalder-Schrader setting relying on measure theory. Relations between different approaches will be discussed.
16-03-2021 | Wacław Marzantowicz: How many vertices we need to triangulate a manifold, part 2
From the beginning of the algebraic topology, then also called the combinatorial topology, i.e. from the beginning of the 20th century, the basic object is the simplicial complex. The representation of a given topological space \(X\) as a simplicial complex (i.e. a homeomorphism with it) is called triangulation. The name comes from the fact that when space \(X\) is a two-dimensional surface, triangulation means representing it as the union of adjacent triangles with edges meeting at the vertices. In the case of higher dimensions, the basic cells are the “i” – dimensional simplices. One of the natural questions is to find a triangulation with the minimum number of vertices, respectively of all simplexes (or estimate these numbers). This lecture will be devoted to this problem. We will present a new method estimating from below the number of vertices by the weighted length of the elements in the cohomology ring \(H^*(X)\).
02-03-2021 | Wacław Marzantowicz: How many vertices we need to triangulate a manifold, part 1
From the beginning of the algebraic topology, then also called the combinatorial topology, i.e. from the beginning of the 20th century, the basic object is the simplicial complex. The representation of a given topological space \(X\) as a simplicial complex (i.e. a homeomorphism with it) is called triangulation. The name comes from the fact that when space \(X\) is a two-dimensional surface, triangulation means representing it as the union of adjacent triangles with edges meeting at the vertices. In the case of higher dimensions, the basic cells are the “i” – dimensional simplices. One of the natural questions is to find a triangulation with the minimum number of vertices, respectively of all simplexes (or estimate these numbers). This lecture will be devoted to this problem. We will present a new method estimating from below the number of vertices by the weighted length of the elements in the cohomology ring \(H^*(X)\).
09-02-2021 | Piotr Maćkowiak: On preserving the domain of a continuous map in its image, part 2
We show some generalizations of the Borsuk theorem according to which for a continuous map \(f\) acting from a compact set \(X\) contained in \(\mathbb R^n\) to \(\mathbb R^n\), if the restriction of \(f\) to the boundary of \(X\) is the identity map, then \(X\) is a subset of the image \(f(X)\). Presented results are coauthored with A. Idzik.
02-02-2021 | Piotr Maćkowiak: On preserving the domain of a continuous map in its image
We show some generalizations of the Borsuk theorem according to which for a continuous map \(f\) acting from a compact set \(X\) contained in \(\mathbb R^n\) to \(\mathbb R^n\), if the restriction of \(f\) to the boundary of \(X\) is the identity map, then \(X\) is a subset of the image \(f(X)\). Presented results are coauthored with A. Idzik.
19-01-2021 | Jacek Gulgowski: Compactness in ΦBV spaces, part 4
The characterization of compact subsets of the space \(\Phi BV\) is given. The characterization refers to the concept of \(\phi\)-equivariated sets.
12-01-2021 | Jacek Gulgowski: Compactness in ΦBV spaces, part 3
The characterization of compact subsets of the space \(\Phi BV\) is given. The characterization refers to the concept of \(\phi\)-equivariated sets.
05-01-2021 | Jacek Gulgowski: Compactness in ΦBV spaces, part 2
The characterization of compact subsets of the space \(\Phi BV\) is given. The characterization refers to the concept of \(\phi\)-equivariated sets.
05-01-2021 | Jerzy Grzybowski: Property of translation and reducibility of minimal pairs of unbounded convex sets, part 3
As pairs of bounded convex sets correspond to ds-functions (differences of sublinear functions) so pairs of unbounded convex sets correspond to dc-functions (differences of convex functions). I am going to present minimal pairs, a property of translation of minimal pairs, a property of reducibility and a relationship between those properties.
22-12-2020 | Jacek Gulgowski: Compactness in ΦBV spaces, part 1
The characterization of compact subsets of the space \(\Phi BV\) is given. The characterization refers to the concept of \(\phi\)-equivariated sets.
15-12-2020 | Jerzy Grzybowski: Property of translation and reducibility of minimal pairs of unbounded convex sets, part 2
As pairs of bounded convex sets correspond to ds-functions (differences of sublinear functions) so pairs of unbounded convex sets correspond to dc-functions (differences of convex functions). I am going to present minimal pairs, a property of translation of minimal pairs, a property of reducibility and a relationship between those properties.
08-12-2020 | Jerzy Grzybowski: Property of translation and reducibility of minimal pairs of unbounded convex sets, part 1
As pairs of bounded convex sets correspond to ds-functions (differences of sublinear functions) so pairs of unbounded convex sets correspond to dc-functions (differences of convex functions). I am going to present minimal pairs, a property of translation of minimal pairs, a property of reducibility and a relationship between those properties.
24-11-2020 | Piotr Kasprzak: On compact integral operators in the space BV, part 3
The aim of the seminar is to fully characterize the class of kernels which generate compact linear integral operators in the BV-space. Using this characterization we show that certain weakly singular and convolution operators (such as the Abel and Volterra operators), when considered as transformations of BV, are compact. We also provide a detailed comparison of those new necessary and sufficient conditions with various other conditions connected with compactness of linear (integral) operators in the space of functions of bounded variation which already exist in the literature.
03-11-2020 | Piotr Kasprzak: On compact integral operators in the space BV, part 2
The aim of the seminar is to fully characterize the class of kernels which generate compact linear integral operators in the BV-space. Using this characterization we show that certain weakly singular and convolution operators (such as the Abel and Volterra operators), when considered as transformations of BV, are compact. We also provide a detailed comparison of those new necessary and sufficient conditions with various other conditions connected with compactness of linear (integral) operators in the space of functions of bounded variation which already exist in the literature.
20-10-2020 | Piotr Kasprzak: On compact integral operators in the space BV, part 1
The aim of the seminar is to fully characterize the class of kernels which generate compact linear integral operators in the BV-space. Using this characterization we show that certain weakly singular and convolution operators (such as the Abel and Volterra operators), when considered as transformations of BV, are compact. We also provide a detailed comparison of those new necessary and sufficient conditions with various other conditions connected with compactness of linear (integral) operators in the space of functions of bounded variation which already exist in the literature.
08-01-2019 | Jin Haixia: The Aleksandrov problem in non-Archimedean 2-fuzzy 2-normed space
We will introduce the concept of isometry which is suitable to represent the notion of area preserving mapping in non-Archimedean 2-fuzzy 2-normed space. Then we obtain some results by applying the Ben’s theorem for the Aleksandrov problem in non-Archimedean 2-fuzzy 2-normed space.
18-12-2018 | Shunxin Zhao: Wigner’s theorem in s space
Wigner theorem is the cornerstone of the mathematical formula of quantum mechanics, it has promoted the research of basic theory of quantum mechanics. In this talk, we give a certain pair of functional equations between two real spaces s, that we called “phase isometry”. It is obtained that all such solutions are phase equivalent to real linear isometries in the spaces.
11-12-2018 | Zhongqin Gao: Omega model for a jump-diffusion process with a two-step premium rate
In this talk, a jump-diffusion Omega model with a two-step premium rate is studied. In this model, the surplus process is a perturbation of a compound Poisson process by a Brown motion. Firstly, using the strong Markov property and Taylor formula, the integro-differential equations for the Gerber-Shiu expected discounted penalty function and the bankruptcy probability are derived. Secondly, for a constant bankruptcy rate function, the renewal equations satisfied by the Gerber-Shiu expected discounted penalty function are obtained, and by iteration, the closed-form solutions of the function are also given. Further, the explicit solutions of the Gerber-Shiu expected discounted penalty function are obtained when the individual claim size is subject to exponential distribution. Finally, a numerical example is presented to illustrate some properties of the model.
04-12-2018 | Xihong Jin (Tianjin University of Technology, Tianjin, China): A variety of Tingley problem in \(\mathcal L^\infty(\Gamma)\)-spaces
During the seminar we are going to prove that for every surjective phaseisometry between the unit spheres of real \(\mathcal L^{\infty}(\Gamma)\)-type spaces, its positive homogeneous extension is a phase-isometry which is phase-equivalent to a linear isometry.
27-11-2018 | Michał Wojtal: Existence of square-mean almost periodic solutions to some stochastic differential equations
We will present certain class of stochastic hyperbolic differential equations with infinite delay. Next, we show existence of square-mean almost periodic solutions to equations of this type using Krasnoselskii’s Fixed Point Theorem. Presentation is based on paper “Existence of square-mean almost periodic solutions to some stochastic hyperbolic differential equations with infinite delay” by P. Bezandry and T. Diagana.
20-11-2018 | Adam Nawrocki: Autonomous superposition operator defined on the space of generalized almost periodic functions
During the seminar we consider the autonomous superposition operator defined on the space of almost periodic functions in view of the Lebesgue measure. In particular, we give connection of this class with the class of the Stepanov almost periodic functions.
13-11-2018 | Adam Nawrocki: Autonomous superposition operator defined on the space of generalized almost periodic functions
During the seminar we consider the autonomous superposition operator defined on the space of almost periodic functions in view of the Lebesgue measure. In particular, we give connection of this class with the class of the Stepanov almost periodic functions.
06-11-2018 | Adam Nawrocki: Some remarks concerning the convolution of a certain almost periodic function
For \(\alpha \in \mathbb R \setminus \mathbb Q\) we define the family of the functions \(f_{\alpha}(x)=1/(2+\cos x + \cos(\alpha x)) \) for \(x \in \mathbb R \). Moreover for \(\lambda<0\) let \(g(x)=e^{\lambda x}\) if \(x\geq 0\) and \(g(x)=0\) if \(x<0\). Then the sets \(S_\lambda=\{\alpha \in \mathbb R\setminus\mathbb Q \, |\,\)the convolution \(f_\alpha \ast g_\lambda \) exists\(\}\) and \(S_\lambda’=\{\alpha \in \mathbb R\setminus\mathbb Q \, |\,\)the convolution \(f_\alpha \ast g_\lambda \) does not exist\(\}\) are dense subsets of \(\mathbb R\). During the seminar we give properties of these sets from the point of view of set theory, measure theory and topology.
30-10-2018 | Adam Nawrocki: Some remarks concerning the convolution of a certain almost periodic function
For \(\alpha \in \mathbb R \setminus \mathbb Q\) we define the family of the functions \(f_{\alpha}(x)=1/(2+\cos x + \cos(\alpha x)) \) for \(x \in \mathbb R \). Moreover for \(\lambda<0\) let \(g(x)=e^{\lambda x}\) if \(x\geq 0\) and \(g(x)=0\) if \(x<0\). Then the sets \(S_\lambda=\{\alpha \in \mathbb R\setminus\mathbb Q \, |\,\)the convolution \(f_\alpha \ast g_\lambda \) exists\(\}\) and \(S_\lambda’=\{\alpha \in \mathbb R\setminus\mathbb Q \, |\,\)the convolution \(f_\alpha \ast g_\lambda \) does not exist\(\}\) are dense subsets of \(\mathbb R\). During the seminar we give properties of these sets from the point of view of set theory, measure theory and topology.
23-10-2018 | Adam Nawrocki: Some remarks concerning the convolution of a certain almost periodic function
For \(\alpha \in \mathbb R \setminus \mathbb Q\) we define the family of the functions \(f_{\alpha}(x)=1/(2+\cos x + \cos(\alpha x)) \) for \(x \in \mathbb R \). Moreover for \(\lambda<0\) let \(g(x)=e^{\lambda x}\) if \(x\geq 0\) and \(g(x)=0\) if \(x<0\). Then the sets \(S_\lambda=\{\alpha \in \mathbb R\setminus\mathbb Q \, |\,\)the convolution \(f_\alpha \ast g_\lambda \) exists\(\}\) and \(S_\lambda’=\{\alpha \in \mathbb R\setminus\mathbb Q \, |\,\)the convolution \(f_\alpha \ast g_\lambda \) does not exist\(\}\) are dense subsets of \(\mathbb R\). During the seminar we give properties of these sets from the point of view of set theory, measure theory and topology.
16-10-2018 | Kosma Kasprzak: About calculating certain limits
In the first part of the talk we will show two ways of calculating the following limit $$\lim_{x \to +\infty} \frac{e^{-x}}{2+\cos x + \cos(\sqrt{2}x)}.$$ In the second part we are going to present some extensions of that result as well as other results connected with this limit.
09-10-2018 | Kosma Kasprzak: About calculating certain limits
In the first part of the talk we will show two ways of calculating the following limit $$\lim_{x \to +\infty} \frac{e^{-x}}{2+\cos x + \cos(\sqrt{2}x)}.$$ In the second part we are going to present some extensions of that result as well as other results connected with this limit.
02-10-2018 | Simon Reinwand: On some Disparities of Multiplication and Composition Operators in BV Spaces
Although multiplication and composition of two functions are first grade operations, the corresponding multiplication and (autonomous) composition operator exhibit many weird and difficult to handle properties in BV spaces. We give criteria for acting conditions, as well as for injectivity, surjectivity, bijectivity and compactness in BV spaces. This leads naturally to a comprehensive study of multiplier sets, of which we will give a short overview. While most of them are easy to determine, some of them – especially those related to classical functions like Darboux and continuous functions – are unknown to our knowledge.
Moreover, we introduce a new type of convergence for composition operators in BV which leads to new a new proof for old continuity criteria. We hope that those ideas can be generalized to other BV-type spaces and give the relevant ideas and conjectures.
Apart from recalling known and discussing new results we put a particular emphasis on examples and counter examples.
19-06-2018 | Ruidong Wang: The Tingley’s Problem on two dimensional normed spaces
In this seminar I will talk about the metric properties of the unit sphere of a two dimensional normed space and the Tingley’s problem on two dimensional normed spaces.
12-06-2018 | Ruidong Wang: The Tingley’s Problem on two dimensional normed spaces
In this seminar I will talk about the metric properties of the unit sphere of a two dimensional normed space and the Tingley’s problem on two dimensional normed spaces.
05-06-2018 | Jacek Gulgowski (Gdańsk University): Integral variation and piecewise polynomial approximation
The concept of integral variation appears to be related to some problems considered in the approximation theory. The concept of polynomials of best approximation leads to certain norm that is equivalent to the q-integral p-variation norm.
29-05-2018 | Xiao-Xiong Gan: From Formal Power Series to Formal Analysis
For any \(l\in \mathbb N\), a formal power series on a ring \(S\) is defined to be a mapping from \(\mathbb N^l\) to \(S\). A formal power series \(f\) in \(x\) from \(\mathbb N\) to \(S\) is usually denoted as a sequence \((a_0,a_1,a_2,\ldots)\) or as a power series \(f(z)=a_0+a_1z+\ldots+a_nz^n+\ldots\), where \(a_j \in S\) for every \(j \in \mathbb N\cup\{0\}\). The set of all formal power series on \(S\) is denoted by \(\mathbb X(S)\).
If considering a formal power series as a sequence, what is the difference between \(\mathbb X\) and \(l^p\)?
If considering a formal power series as a power series, what is the difference between formal power series and the traditional power series? What is the relationship between formal power series and traditional power series?
What is formal analysis?
This talk tries to answer those questions and brings discussion of all kinds of questions about formal analysis, a relatively new mathematical subject.
08-05-2018 | Michał Wojtal: Introduction to stochastic integral
During the talk we will discuss the construction of stochastic integral and it’s basic properties.
24-04-2018 | Ruidong Wang: On isometric extension problem on the unit sphere of normed spaces
The isometric extension problem has been studied by a number of mathematicians, and there are many deep and interesting partial results, even this problem has not been solved till now.
17-04-2018 | Ruidong Wang: On isometric extension problem on the unit sphere of normed spaces
The isometric extension problem has been studied by a number of mathematicians, and there are many deep and interesting partial results, even this problem has not been solved till now.
10-04-2018 | Ruidong Wang: On isometric extension problem on the unit sphere of normed spaces
The isometric extension problem has been studied by a number of mathematicians, and there are many deep and interesting partial results, even this problem has not been solved till now.
27-03-2018 | Michał Wojtal: Introduction to stochastic integral
During the talk we will discuss the construction of stochastic integral and it’s basic properties.
13-03-2018 | Marcin Borkowski: On partial metric spaces
The talk will be devoted to basic properties of so-called partial metric spaces and to proving a variant of the Banach contraction principle for such spaces. The talk is based on a paper /Parrtial metric topology/ by S. G. Matthews.
06-03-2018 | Marcin Borkowski: On partial metric spaces
The talk will be devoted to basic properties of so-called partial metric spaces and to proving a variant of the Banach contraction principle for such spaces. The talk is based on a paper /Parrtial metric topology/ by S. G. Matthews.
27-02-2018 | Michał Wojtal: Introduction to stochastic integral
During the talk we will discuss the construction of stochastic integral and it’s basic properties.
30-01-2018 | Michał Wojtal: Introduction to stochastic integral
During the talk we will discuss the construction of stochastic integral and it’s basic properties.
16-01-2018 | Michał Wojtal: Introduction to stochastic integral
During the talk we will discuss the construction of stochastic integral and it’s basic properties.
09-01-2018 | Piotr Kasprzak: On a certain fixed point theorem in Banach algebras
During the seminar we are going to discuss a certain version of the Krasnoselskii fixed point theorem for the sum of two operators in Banach algebras.
05-01-2018 | Jian Meng (Tianjin University of Technology, China): On some binomial difference sequence spaces
The matrix domains of Cesàro mean, Riesz mean 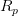 , Nörlund mean
, Nörlund mean 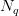 and Euler mean of order r in the sequence spaces
and Euler mean of order r in the sequence spaces 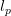 ,
, 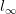 , c and
, c and 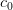 have been studied by some authors. The Binomial mean is one of the most important methods in the summability theory, but the matrix domain of binomial mean has not been studied, until now. The aim of this talk is to introduce the binomial difference sequence spaces. We prove some basic properties of these spaces and some inclusion relations. Moreover, we obtain the Schauder bases of some of these spaces and compute the α-, β- and γ-duals of these sequence spaces.
have been studied by some authors. The Binomial mean is one of the most important methods in the summability theory, but the matrix domain of binomial mean has not been studied, until now. The aim of this talk is to introduce the binomial difference sequence spaces. We prove some basic properties of these spaces and some inclusion relations. Moreover, we obtain the Schauder bases of some of these spaces and compute the α-, β- and γ-duals of these sequence spaces.
19-12-2017 |dr Jacek Gulgowski: Continuity of nonautonomous superposition operator in Lambda BV spaces
We are going to present sufficient conditions for the continuity of the nonautonomous superposition operator acting in Lambda BV spaces. The conditions cover generators of class 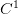 in two variables, but allow also for much broader class of functions.
in two variables, but allow also for much broader class of functions.
28-11-2017 | Marcin Borkowski: On partial metric spaces
The talk will be devoted to basic properties of so-called partial metric spaces and to proving a variant of the Banach contraction principle for such spaces. The talk is based on a paper /Parrtial metric topology/ by S. G. Matthews.
21-11-2017 | Piotr Kasprzak: On weak topology in the space BV[0,1]
The aim of the seminar is to present a characterization of the weak convergence in the space of functions of bounded Jordan variation. We are also going to discuss the weak compactness in such spaces.
24-10-2017 | Piotr Kasprzak: On weak topology in the space BV[0,1]
The aim of the seminar is to present a characterization of the weak convergence in the space of functions of bounded Jordan variation. We are also going to discuss the weak compactness in such spaces.
17-10-2017 | Piotr Kasprzak: On weak topology in the space BV[0,1]
The aim of the seminar is to present a characterization of the weak convergence in the space of functions of bounded Jordan variation. We are also going to discuss the weak compactness in such spaces.
10-10-2017 |Simon Reinwand (University of Würzburg): On Functions with Primitives
The problem of characterizing those functions, which possess a classical primitive has been investigated for decades. As far as we know, it is still an open problem if there is a “natural” characterization without involving integrals.
In this talk we give a quick overview about different characterizations while keeping our focus on probably the most natural one involving the Henstock-Kurzweil Integration Theory. While being a slight generalization of the Riemann Integral, it provides not only the most comprehensive version of the classical Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, but also yields a full characterization of the class of functions, which have a primitive.
We will discuss this class in more detail with respect to its size, its relation to other function classes, and some of its algebraic properties. Apart from recalling known and discussing new results we put a particular emphasis on examples and counter examples.
While answering questions regarding multiplication and change of variables we will point out connections between functions with primitives, Darboux-functions, HK-integrable functions and functions of bounded variation.
06-06-2017 | Piotr Kasprzak: On weak topology in the space BV[0,1]
The aim of the seminar is to present a characterization of the weak convergence in the space of functions of bounded Jordan variation. We are also going to discuss the weak compactness in such spaces.
16-05-2017 | Marcin Borkowski: On 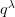 -hyperconvex quasi-metric spaces
-hyperconvex quasi-metric spaces
The aim of the talk is to introduce the definition and basic properties
of quasi-metric spaces and the notion of 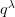 -hyperconvexity in
-hyperconvexity in
these spaces.
09-05-2017 | Marcin Borkowski: On 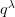 -hyperconvex quasi-metric spaces
-hyperconvex quasi-metric spaces
The aim of the talk is to introduce the definition and basic properties
of quasi-metric spaces and the notion of 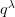 -hyperconvexity in
-hyperconvexity in
these spaces.
11-04-2017 | Marcin Borkowski: On 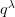 -hyperconvex quasi-metric spaces
-hyperconvex quasi-metric spaces
The aim of the talk is to introduce the definition and basic properties
of quasi-metric spaces and the notion of 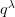 -hyperconvexity in
-hyperconvexity in
these spaces.
04-04-2017 | Marcin Borkowski: On 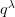 -hyperconvex quasi-metric spaces
-hyperconvex quasi-metric spaces
The aim of the talk is to introduce the definition and basic properties
of quasi-metric spaces and the notion of 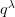 -hyperconvexity in
-hyperconvexity in
these spaces.
21-03-2017 | Marcin Borkowski: On some metric spaces
During the talk we will present certain construction of metric spaces,
described by Száz and generalizing the linking construction known
from Aksoy and Maurizi’s paper. We will then proceed to examine some of
its properties, in particular connected with measures of noncompactness.
14-03-2017 | Michał Goliński: Formal power series (Part 1)
At the seminar we will discuss the following statement of M. Artin:
Let 3d0202424.png) be analytic equation (
be analytic equation (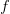 is analytic). We will show that if the equation has a solution
is analytic). We will show that if the equation has a solution 202424.png) in the space of formal series than it has also analytic solution which differs from
in the space of formal series than it has also analytic solution which differs from 20202424.png) coefficients with large powers.
coefficients with large powers.
07-03-2017 | Michał Goliński: Formal power series (Part 1)
At the seminar we will discuss the following statement of M. Artin:
Let 3d0202424.png) be analytic equation (
be analytic equation (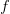 is analytic). We will show that if the equation has a solution
is analytic). We will show that if the equation has a solution 202424.png) in the space of formal series than it has also analytic solution which differs from
in the space of formal series than it has also analytic solution which differs from 20202424.png) coefficients with large powers.
coefficients with large powers.
28-02-2017 | Marcin Borkowski: On some metric spaces
During the talk we will present certain construction of metric spaces,
described by Száz and generalizing the linking construction known
from Aksoy and Maurizi’s paper. We will then proceed to examine some of
its properties, in particular connected with measures of noncompactness.
31-01-2017 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Action and continuity of superposition operators
During the seminar we will present results from the book R.M. Dudley, R. Norvaisa, Concrete functional calculus (Springer 2011) concerning conditions for the action and continuity of superposition operators acting in the space of functions of bounded variation in the Jordan sense.
24-01-2017 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Action and continuity of superposition operators
During the seminar we will present results from the book R.M. Dudley, R. Norvaisa, Concrete functional calculus (Springer 2011) concerning conditions for the action and continuity of superposition operators acting in the space of functions of bounded variation in the Jordan sense.
17-01-2017 | Marcin Borkowski: On some measures of efficiency of financial projects
A classic – and the most well-known – measure of efficiency of financial
projects is the net present value (NPV). However, it has certain issues
connected with choosing the “right” discount rate. In the paper by
Teichroew et al. (1965) it was shown how to compute net future value
using two rates: one for financing and one for reinvesting. The authors
mention how to use their method to compute an analogue of the NPV.
Unfortunately, their method is wrong. The first part of the talk will
be devoted to showing their error and comparing their method to
a correct one due to A. Kulakova (2010). Then, we will prove a number
of properties of the generalized net present value defined by the latter
author.
10-01-2017 | Meng Liu: On the Generalized Hyers-Ulam-Rassias Stability of an k-Dimensional Quadratic Functional Equation
In this lecture, we investigate the generalized Hyers-Ulam-Rassias stability of an k- dimensional quadratic functional equation. At the same time, we will generalize the theorem of Jae-Hyeong Bae and Kil-Woung Jun. We also get Hyers-Ulam-Rassias stability of the k-dimensional quadratic functional equation in restricted domains.
03-01-2017 | Marcin Borkowski: On some measures of efficiency of financial projects
A classic – and the most well-known – measure of efficiency of financial
projects is the net present value (NPV). However, it has certain issues
connected with choosing the “right” discount rate. In the paper by
Teichroew et al. (1965) it was shown how to compute net future value
using two rates: one for financing and one for reinvesting. The authors
mention how to use their method to compute an analogue of the NPV.
Unfortunately, their method is wrong. The first part of the talk will
be devoted to showing their error and comparing their method to
a correct one due to A. Kulakova (2010). Then, we will prove a number
of properties of the generalized net present value defined by the latter
author.
20-12-2016 | Meng Liu: Generalized stability of an AQ-functional equation in
quasi-(2;p)-Banach spaces
The stability of functional equation is a vital subject of functional
analysis. We introduce and investigate the general solution of a new
functional equation -AQ functional equation and discuss its Generalized
Hyers-Ulam-Rassias stability under the conditions such as even, odd,
approximately even and approximately odd in quasi-(2;p)-Banach spaces.
13-12-2016 | Marcin Borkowski: On some measures of efficiency of financial projects
A classic – and the most well-known – measure of efficiency of financial
projects is the net present value (NPV). However, it has certain issues
connected with choosing the “right” discount rate. In the paper by
Teichroew et al. (1965) it was shown how to compute net future value
using two rates: one for financing and one for reinvesting. The authors
mention how to use their method to compute an analogue of the NPV.
Unfortunately, their method is wrong. The first part of the talk will
be devoted to showing their error and comparing their method to
a correct one due to A. Kulakova (2010). Then, we will prove a number
of properties of the generalized net present value defined by the latter
author.
06-12-2016 | dr Giselle Monteiro (Slovak Academy of Sciences): Extremal solutions for measure differential equations
We investigate the existence of greatest and least solutions for the so-called measure differential equations – namely, integral equations in which the Stieltjes type integral is in the sense of Kurzweil. Based on these results, we derive new theorems about extremal solutions for impulsive systems.
Acknowledgement: Research financed by the SASPRO Programme, co-financed by the European Union and the Slovak Academy of Sciences.
29-11-2016 | Jacek Gulgowski: On functions of bounded 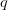 -integral
-integral 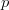 -variation
-variation
During the seminar we are going to discuss functions of bounded 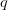 -integral
-integral 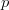 -variation. In particular, we are going to present some of their basic properties. We are also going to discuss the relationship of the space of such functions with Sobolev spaces. Finally, we are going to show some results on superposition operator and nonlinear integral operator acting in the space of functions of bounded
-variation. In particular, we are going to present some of their basic properties. We are also going to discuss the relationship of the space of such functions with Sobolev spaces. Finally, we are going to show some results on superposition operator and nonlinear integral operator acting in the space of functions of bounded 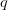 -integral
-integral 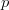 -variation.
-variation.
15-11-2016 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Action and continuity of superposition operators
During the seminar we will present results from the book R.M. Dudley, R. Norvaisa, Concrete functional calculus (Springer 2011) concerning conditions for the action and continuity of superposition operators acting in the space of functions of bounded variation in the Jordan sense.
08-11-2016 | Monika Naskręcka: Necessary and sufficient conditions of stability some particular differential equations system
During this seminar we will present lemmas and theorems which are necessary and sufficient conditions of stability some particular differential equations system with discontinuous right-hand side, which describe the dynamics of prices and stocks.
25-10-2016 | Monika Naskręcka: Necessary and sufficient conditions of stability some particular differential equations system
During this seminar we will present lemmas and theorems which are necessary and sufficient conditions of stability some particular differential equations system with discontinuous right-hand side, which describe the dynamics of prices and stocks.
18-10-2016 | Monika Naskręcka: Necessary and sufficient conditions of stability some particular differential equations system
During this seminar we will present lemmas and theorems which are necessary and sufficient conditions of stability some particular differential equations system with discontinuous right-hand side, which describe the dynamics of prices and stocks.
11-10-2016 | Marcin Borkowski: On some metric spaces
During the talk we will present certain construction of metric spaces,
described by Száz and generalizing the linking construction known
from Aksoy and Maurizi’s paper. We will then proceed to examine some of
its properties, in particular connected with measures of noncompactness.
04-10-2016 | Marcin Borkowski: On some metric spaces
During the talk we will present certain construction of metric spaces,
described by Száz and generalizing the linking construction known
from Aksoy and Maurizi’s paper. We will then proceed to examine some of
its properties, in particular connected with measures of noncompactness.
14-06-2016 | Marcin Borkowski: On hyperconvex hull of diversities
The talk will be devoted to problems with introducing the analogue of
hyperconvex hull (equivalently, tight span) of a diversity.
07-06-2016 | Marcin Borkowski: On hyperconvex hull of diversities
The talk will be devoted to problems with introducing the analogue of
hyperconvex hull (equivalently, tight span) of a diversity.
31-05-2016 | Lech Pasicki: Classical fixed point theorems
Author’s extensions of the well-known fixed point theorems will be presented. The theorem of Banach, the theorem of Caristi (also with the variational results), and the theorem of Browder-Göhde-Kirk for nonexpansive mappings are involved. Our versions extend these theorems, as their specific assumptions are weaker, and the spaces under consideration are more general.
26-04-2016 | Adam Nawrocki: Levitan almost periodic solutions to some linear differential equation
During this lecture we will show that a Levitan almost periodic (briefly: LAP) solution to the equation 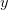 ‘
‘3d5clambda20y(x)2bf(x)202424.png) usually can be expressed by means of convolution. We will show that in this way we can get an unbounded LAP solution. We will give an example showing that the convolution in not always a good tool to look for LAP solutions.
usually can be expressed by means of convolution. We will show that in this way we can get an unbounded LAP solution. We will give an example showing that the convolution in not always a good tool to look for LAP solutions.
19-04-2016 | Adam Nawrocki: Levitan almost periodic solutions to some linear differential equation
During this lecture we will show that a Levitan almost periodic (briefly: LAP) solution to the equation 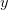 ‘
‘3d5clambda20y(x)2bf(x)202424.png) usually can be expressed by means of convolution. We will show that in this way we can get an unbounded LAP solution. We will give an example showing that the convolution in not always a good tool to look for LAP solutions.
usually can be expressed by means of convolution. We will show that in this way we can get an unbounded LAP solution. We will give an example showing that the convolution in not always a good tool to look for LAP solutions.
12-04-2016 | Marcin Borkowski: Another look at hyperconvex hulls
The talk will be devoted to a certain generalization of the notion of
a metric space, inspired by applications to taxonomy, in which one can
introsuce an analogue of the notion of hyperconvexity. We will start
with an a bit atypical angle on Isbell’s hyperconvex hull, and then we
will proceed to describe some problems with transferring his ideas to
the generalization in question.
05-04-2016 | Albert Kubzdela: On some properties of some measure of non-compactness in non-Archimedean analysis
Let  be a locally compact non-Archimedean field, and
be a locally compact non-Archimedean field, and  a non-Archimedean Banach space over
a non-Archimedean Banach space over  . We define non-Archimedean equivalents of several well-known measures of non-compactness defined on
. We define non-Archimedean equivalents of several well-known measures of non-compactness defined on  , we describe their properties and we present quantitative versions of several classic statements on weak compactness (theorems of Krein, Gantmacher and Grothendieck) for non-Archimedean Banach spaces.
, we describe their properties and we present quantitative versions of several classic statements on weak compactness (theorems of Krein, Gantmacher and Grothendieck) for non-Archimedean Banach spaces.
22-03-2016 | Adam Nawrocki: The autonomous superposition operator defined on the space of almost periodic functions in view of the Lebesgue measure
During this lecture we shall discuss autonomuous superposition operators generated by mappings 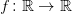 and acting in the space of
and acting in the space of 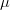 -almost periodic functions.
-almost periodic functions.
15-03-2016 | Adam Nawrocki: The autonomous superposition operator defined on the space of almost periodic functions in view of the Lebesgue measure
During this lecture we shall discuss autonomuous superposition operators generated by mappings 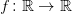 and acting in the space of
and acting in the space of 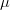 -almost periodic functions.
-almost periodic functions.
08-03-2016 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Continuity of the non-autonomous superposition operator and around
We shall present an example of a function ![$$ f:[0,1]\times\mathbb R\to \mathbb R $$](http://octd.wmi.amu.edu.pl/latex/242420f3a5b02c15d5ctimes5cmathbb20R5cto205cmathbb20R202424.png) which is lipschitzian and such that the (non-autonomous) superposition operator it generates is not continuous (as a mapping from
which is lipschitzian and such that the (non-autonomous) superposition operator it generates is not continuous (as a mapping from 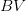 to
to 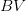 ). We shall show necessary and sufficient conditions for a non-autonomous superposition operator to be continuous (in
). We shall show necessary and sufficient conditions for a non-autonomous superposition operator to be continuous (in 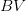 ). We shall also prove some results for
). We shall also prove some results for 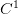 -class generators.
-class generators.
01-03-2016 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Continuity of the non-autonomous superposition operator and around
We shall present an example of a function ![$$ f:[0,1]\times\mathbb R\to \mathbb R $$](http://octd.wmi.amu.edu.pl/latex/242420f3a5b02c15d5ctimes5cmathbb20R5cto205cmathbb20R202424.png) which is lipschitzian and such that the (non-autonomous) superposition operator it generates is not continuous (as a mapping from
which is lipschitzian and such that the (non-autonomous) superposition operator it generates is not continuous (as a mapping from 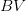 to
to 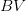 ). We shall show necessary and sufficient conditions for a non-autonomous superposition operator to be continuous (in
). We shall show necessary and sufficient conditions for a non-autonomous superposition operator to be continuous (in 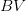 ). We shall also prove some results for
). We shall also prove some results for 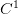 -class generators.
-class generators.
26-01-2016 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Continuity of the non-autonomous superposition operator and around
We shall present an example of a function ![$$ f:[0,1]\times\mathbb R\to \mathbb R $$](http://octd.wmi.amu.edu.pl/latex/242420f3a5b02c15d5ctimes5cmathbb20R5cto205cmathbb20R202424.png) which is lipschitzian and such that the (non-autonomous) superposition operator it generates is not continuous (as a mapping from
which is lipschitzian and such that the (non-autonomous) superposition operator it generates is not continuous (as a mapping from 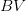 to
to 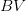 ). We shall show necessary and sufficient conditions for a non-autonomous superposition operator to be continuous (in
). We shall show necessary and sufficient conditions for a non-autonomous superposition operator to be continuous (in 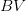 ). We shall also prove some results for
). We shall also prove some results for 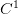 -class generators.
-class generators.
19-01-2016 | Marcin Borkowski: On some fixed point theorem in ultrametric spaces
We will discuss a theorem establishing the existence of a fixed point and a (generalized) sequence approximating this fixed point. The talk is based in a paper by S. Priess-Crampe and P. Ribenboim from 2013.
12-01-2016 | Marcin Borkowski: On some fixed point theorem in ultrametric spaces
We will discuss a theorem establishing the existence of a fixed point and a (generalized) sequence approximating this fixed point. The talk is based in a paper by S. Priess-Crampe and P. Ribenboim from 2013.
15-12-2015 | Marcin Borkowski: On some fixed point theorem in ultrametric spaces
We will discuss a theorem establishing the existence of a fixed point and a (generalized) sequence approximating this fixed point. The talk is based in a paper by S. Priess-Crampe and P. Ribenboim from 2013.
08-12-2015 | Mateusz Krukowski: Darbo type theorem for quasi-measures of non-compactness.
This presentation introduces the notion of a quasi-measure of non-compactness. Such functions need not to be invariant in a convex hull in contrast to classical measures of non-compactness. Using the compactness criterion in the space \(BC(X,E)\) (\(X,E\)are Banach spaces with \(\dim(X)<\infty\))), we construct a quasi-measure of non-compactness and study its properties. Furthermore we prove the analog of the Darbo theorem using the measure of non-convexity. We also show the application of the shown tools to finding a fixed point of the Hammerstein operator.
01-12-2015 | Paweł Kliber: Consumer choices using hyperbolic discounting – the model and Euler conditions.
This presentation concerns an article in which the problem of choosing the consumption path for a consumer using hyperbolic discounting (he treats the present and the whole future differently) in a model with random rate of return is discussed. The model, along with assumptions and the most important properties of the solution are presented.
17-11-2015 | Paweł Kliber: Consumer choices using hyperbolic discounting – the model and Euler conditions.
This presentation concerns an article in which the problem of choosing the consumption path for a consumer using hyperbolic discounting (he treats the present and the whole future differently) in a model with random rate of return is discussed. The model, along with assumptions and the most important properties of the solution are presented.
10-11-2015 | Paweł Kliber: Consumer choices using hyperbolic discounting – the model and Euler conditions.
This presentation concerns an article in which the problem of choosing the consumption path for a consumer using hyperbolic discounting (he treats the present and the whole future differently) in a model with random rate of return is discussed. The model, along with assumptions and the most important properties of the solution are presented.
03-11-2015 | Paweł Kliber: Consumer choices using hyperbolic discounting – the model and Euler conditions.
This presentation concerns an article in which the problem of choosing the consumption path for a consumer using hyperbolic discounting (he treats the present and the whole future differently) in a model with random rate of return is discussed. The model, along with assumptions and the most important properties of the solution are presented.
27-10-2015 | Elżbieta Gajecka: Resampling methods in the time domain for time series with periodic and almost periodic structure.
(The seminar will be held in room B3-38)
Statistical reasoning, in the case of time series, based on asymptotic distributions cannot always be a basis for effective statistical procedures. However unknown distributions of estimators or statistics can be approximated by the so-called resampling procedures. The idea of resampling methods is obtaining replications of the estimator and calculating the empirical distribution from those replications. The main question, to be answered, is whether this empirical distribution, called the resampling distribution, is close to the real distribution.
Intense research is being conducted towards resampling methods in nonstationary time series, in particular series with periodic and almost periodic structure. During this seminar various methods of resampling, especially subsampling, will be shown. The advantage of subsampling is its insensitivity to the shape of the asymptotic distribution. We will also show conditions of compatibility of resampling methods in the domain of time for 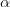 -mixing or weakly dependent time series with periodic or almost periodic structure. Especially weak dependency gives new tools to analyse statistical procedures for very general data generating time series, together with periodic series with long memory and heavy tails. An example of a periodic model with heavy tails and long memory will be shown.
-mixing or weakly dependent time series with periodic or almost periodic structure. Especially weak dependency gives new tools to analyse statistical procedures for very general data generating time series, together with periodic series with long memory and heavy tails. An example of a periodic model with heavy tails and long memory will be shown.
20-10-2015 | Paweł Kliber: Consumer choices using hyperbolic discounting – the model and Euler conditions.
This presentation concerns an article in which the problem of choosing the consumption path for a consumer using hyperbolic discounting (he treats the present and the whole future differently) in a model with random rate of return is discussed. The model, along with assumptions and the most important properties of the solution are presented.
13-10-2015 | Piotr Kasprzak: Abel’s integral equation
The aim of the talk is to discuss mathematical background for the theory of Abel’s integral equation and to present some of its real world applications.
06-10-2015 | Piotr Kasprzak: Abel’s integral equation
The aim of the talk is to discuss mathematical background for the theory of Abel’s integral equation and to present some of its real world applications.
09-06-2015 | Adam Nawrocki: Doubly periodic functions
During this seminar we shall discuss the notion of doubly periodic functions and almost periodic functions in the context of elliptic functions.
02-06-2015 | Xiao-Xiong Gan: Some Remarks on Minkowski’s Inequality
The classical Minkowski’s inequality has two different forms based on the values of the positive number \(p\):
- If \(1\leq p < \infty\), then \(\|f+g\|_p \leq \|f\|_p + \|g\|_p\);
- If \(0< p < 1\), then \(\|f+g\|_p \geq \|f\|_p + \|g\|_p\).
We provide a one-form Minkowski’s inequality for all \(p>0\). A non-conjugate Hölder’s inequality is also introduced. Some applications of the one-form Minkowski’s inequality and non-conjugate Hölder’s inequality are introduced too.
19-05-2015 | Patryk Kołacki: Sliding mode control in automatic control systems
In this seminar, I’m going to present you on the most popular control laws, i.e. sliding mode control. There will be discussed it’s basic, canonical form and it’s most popular applications. I also want to show a few examples which let you understand the idea of this control law.
12-05-2015 | Patryk Kołacki: Sliding mode control in automatic control systems
In this seminar, I’m going to present you on the most popular control laws, i.e. sliding mode control. There will be discussed it’s basic, canonical form and it’s most popular applications. I also want to show a few examples which let you understand the idea of this control law.
05-05-2015 | Adam Nawrocki: Doubly periodic functions
During this seminar we shall discuss the notion of doubly periodic functions and almost periodic functions in the context of elliptic functions.
28-04-2015 | Adam Nawrocki: Doubly periodic functions
During this seminar we shall discuss the notion of doubly periodic functions and almost periodic functions in the context of elliptic functions.
21-04-2015 | dr Przemysław Chełminiak: What connects a biological cell with a partial diffusion equation.
Tracking individual molecules in living biological cells has become possible today by a new imaging technique called single-molecule spectroscopy. Interestingly, a diffusion of such tiny nano-molecules as proteins, nucleic acids or semiflexible polymers within a dense cellular environment is slower than ordinary Brownian diffusion of the micro-particles suspended in water. Their spatial development inside the cell, characterized by the time or ensemble averaged mean squared displacements, does not grow linearly in time. Moreover, these two averaging procedures are not equivalent when the measurement time is long compared to the characteristic time scale of the diffusion process. Therefore, the erratic motion of the subcellular molecules can not be perceived as a typical Brownian motion, but it must be considered in terms of the anomalous diffusion (subdiffusion). From a formal point of view, the anomalous diffusion can be described by a widely applicable stochastic process known as the continuous-time random walk model. We apply this method to construct the so called fractional Fokker-Planck equation which is an extended version of the subdiffusion equation in an external force field and close to thermal equilibrium. Using the methods of fractional calculus we find a few special solutions of this fractional partial differential equation and show that the mean squared displacement of a subdiffusing particle scales with time according to the power-law.
14-04-2015 | dr Giselle Monteiro: New convergence theorem for the abstract Kurzweil-Stieltjes integral
In theory of Riemann integral, the impact of the Bounded Convergence Theorem, also called Arzela or Arzela-Osgood or Osgood Theorem, is comparable to the importance of the Lebesgue Dominated convergence Theorem in the theory of the Lebesgue integration. In this talk we are concerned with the abstract Kurzweil-Stieltjes integral, that is, the Stieltjes type integral for functions with values in a Banach space introduced by S. Schwabik. Our aim is to present the Bounded Convergence Theorem in this general setting.
31-03-2015 | Piotr Maćkowiak: A combinatorial lemma ant it’s consequences
During this seminar we shall introduce a combinatorial lemma stating the existence for particular triangulations of the \((n-1)\)-dimensional simplex with a particular labeling of vertices of such triangulations with numbers \(\{0,1,\ldots,n\}\) of a chain of simplices connecting a “vartex” with a “base” such that for any simplex from that chain each element of the set \(\{1,\ldots,n-1\}\) is a label of some vertex of that simplex. We shall show, that (simple) consequences of this lemma are:
- the existence of zeros of the multidimensional function of excess demand
- the existence of continuum zeros of the parametrised multidimensional function of excess demand
- the well-known Sperner lemma
24-03-2015 | Marcin Borkowski: On a generalisation of a metric space
During this seminar we shall give the axioms of a diversity, which generalises the notion of metric spaces. We shall give examples of diversities and prove some of their properties.
17-03-2015 | Piotr Maćkowiak: A combinatorial lemma ant it’s consequences
During this seminar we shall introduce a combinatorial lemma stating the existence for particular triangulations of the \((n-1)\)-dimensional simplex with a particular labeling of vertices of such triangulations with numbers \(\{0,1,\ldots,n\}\) of a chain of simplices connecting a “vartex” with a “base” such that for any simplex from that chain each element of the set \(\{1,\ldots,n-1\}\) is a label of some vertex of that simplex. We shall show, that (simple) consequences of this lemma are:
- the existence of zeros of the multidimensional function of excess demand
- the existence of continuum zeros of the parametrised multidimensional function of excess demand
- the well-known Sperner lemma
10-03-2015 | Marcin Borkowski: On a generalisation of a metric space
During this seminar we shall give the axioms of a diversity, which generalises the notion of metric spaces. We shall give examples of diversities and prove some of their properties.
03-03-2015 | Jędrzej Sadowski: Quasicrystals and almost periodic patterns
During this seminar we shall introduce the definition of almost periodic patterns, their basic properties and connection to quasicrystals.
24-02-2015 | dr Jacek Gulgowski: Compactness in spaces of functions of bounded variation.
The studies on the existence of fixed points of mappings in Banach spaces often involve methods connected with the Schauder fixed point theorem or the Leray-Schauder degree. Both approaches require the considered mappings to be completely continuous, and therefore, if one wants to work in spaces of functions of bounded variation, it is crucial to understand the mutual relations between \(\Lambda BV(I)\) and \(BV_{\phi}(I)\) spaces. During the seminar we are going to discuss certain results on compact embeddings of such spaces and characterise the complete continuity of some nonlinear integral operators acting in \(BV_p(I)\) spaces.
27-01-2015 | Jędrzej Sadowski: Quasicrystals and almost periodic patterns
During this seminar we shall introduce the definition of almost periodic patterns, their basic properties and connection to quasicrystals.
20-01-2015 | Jędrzej Sadowski: Quasicrystals and almost periodic patterns
During this seminar we shall introduce the definition of almost periodic patterns, their basic properties and connection to quasicrystals.
13-01-2015 | Jędrzej Sadowski: Quasicrystals and almost periodic patterns
During this seminar we shall introduce the definition of almost periodic patterns, their basic properties and connection to quasicrystals.
09-12-2014 | Monika Naskręcka: The existence of solutions of a certain system of differential equations with discontinuous right-hand side.
During this seminar we will discuss the existence of solutions of a certain system of differential equations with discontinuous right-hand side. This system depicts the dynamics of supplies in a model of competitive economy.
02-12-2014 | Marcin Borkowski: On a certain fixed point theorem for ultrametric spaces
We will discuss some variant of the Banach Contraction Principle, announced by N. Ackerman, for ultrametric spaces with metrics with values in a complete lattice.
25-11-2014 | dr Przemysław Chełminiak: Stochastic dynamics of self-organizing critical nets
Self-organizing critical nets have been an object of intense research for over 15 years. They possess many peculiar properties, namely: fractality, self-similarity, topological criticality, little world effect and they are scale-free, which follow from their stochastic evolution. It occurs that many of such nets exist in an unstable state on the boundary of two phases, small-fractal world. Methods of construction and analysing critical nest will be shown, along with basic properties of probability distributions of stationary streams following stochastic dynamics of such nets.
18-11-2014 | Marcin Borkowski: On a certain fixed point theorem for ultrametric spaces
We will discuss some variant of the Banach Contraction Principle, announced by N. Ackerman, for ultrametric spaces with metrics with values in a complete lattice.
04-11-2014 | Marcin Borkowski: On a certain fixed point theorem for ultrametric spaces
We will discuss some variant of the Banach Contraction Principle, announced by N. Ackerman, for ultrametric spaces with metrics with values in a complete lattice.
28-10-2014 | Dr Mateusz Maciejewski: Existence of positive solutions of systems of parabolic equations with non-local initial conditions.
The topic of this speech is the existence of positive solutions of systems of parabolic equations with the boundary Dirichlet conditions and non-local initial conditions. For this purpose I shall show a fixed point theorem, which proof is based on Granas’ fixed-point index. Thanks to the possibility of localisation of solutions I shall receive a theorem about existence of more than one solution.
21-10-2014 | Marcin Borkowski: Fixed point theorems with a boundary condition
In 1998, Espínola and López proved a certain fixed point theorem for a mapping transforming an admissible subset \(A\) of a hyperconvex metric space into the whole space, assuming that this mapping sends the boundary of \(A\) into \(A\). We will show how to simplify their proof considerably, at the same time relaxing its assumptions. In particular, this will enable proving a new fixed point theorem, generalizing a classical result of Baillon from 1988.
14-10-2014 | Piotr Kasprzak: The game of Hex and the Brouwer fixed-point theorem.
During the seminar we are going to porve show that the celebrated Boruwer fixed-point theorem is a consequence of the fat that Hex cannot end in a draw.
07-10-2014 | Marcin Borkowski: Fixed point theorems with a boundary condition
In 1998, Espínola and López proved a certain fixed point theorem for a mapping transforming an admissible subset \(A\) of a hyperconvex metric space into the whole space, assuming that this mapping sends the boundary of \(A\) into \(A\). We will show how to simplify their proof considerably, at the same time relaxing its assumptions. In particular, this will enable proving a new fixed point theorem, generalizing a classical result of Baillon from 1988.
30-09-2014 | prof. Gennaro Infante: Nontrivial solutions of perturbed Hammerstein integral equations
We discuss the existence of positive solutions of some perturbed Hammerstein integral equations by means of classical fixed point index theory.We apply our results to some nonlocal BVPs that arise in some heat flow problems to prove the existence of multiple positive solutions under suitable conditions. We also illustrate how this approach might be applied to different problems.
16-09-2014 | Dariusz Bugajewski: BV-solutions of nonlinear equations
During the seminar we are going to prove the existence of BV-solutions to several nonlinear equations using the fixed point approach.
10-06-2014 | Adam Nawrocki: The convolution operator defined on the space of Levitan almost periodic functions.
It is known, that the convolution of a bounded, Levitan almost periodic function with a \(L^1(\mathbb R)\) function is a bounded, Levitan almost periodic function. During this lecture we shall discuss the result we will receive when unbounded Levitan almost periodic functions are used.
27-05-2014 | Adam Nawrocki: The convolution operator defined on the space of Levitan almost periodic functions.
It is known, that the convolution of a bounded, Levitan almost periodic function with a \(L^1(\mathbb R)\) function is a bounded, Levitan almost periodic function. During this lecture we shall discuss the result we will receive when unbounded Levitan almost periodic functions are used.
20-05-2014 | Adam Nawrocki: Asymptotic behaviour of a certain almost periodic function with regard to the Lebesgue measure
The function \[ f(x)=\frac{1}{2+\cos{x}+\cos(x\sqrt{2})}\] is a classical example of an unbounded and continuous \(\mu\)-almost periodic function. For this function we have
\[\forall \varepsilon>0 \lim_{x \to \infty}x^{-2-\varepsilon}f(x)=0\]
During this lecture we will discuss the idea of the proof of the equality above, which uses diophantic approximations. We shall furthermore show, that the limit\[ \lim_{x \to \infty}x^{-2}f(x)=0\] will not exist.
06-05-2014 | Monika Naskręcka: Mathematical model of a competitive market with stocks.
Equilibrium and stability are the most frequently investigated properties in the market equilibrium models. On global and local markets we usually observe the lack of equilibrium. Nevertheless, the original model does not consider the possibility of stocks. However, we observe this situation, when there exists an excess supply. We should consider then how the accumulated stocks affect the equilibrium (or disequilibrium) and the stability of the model. During the seminar I will present the competitive economy model and the model with stocks. I will explore how these stocks influence the path of the price trajectory, equilibrium conditions and price stability.
29-04-2014 | Monika Naskręcka: Mathematical model of a competitive market with stocks.
Equilibrium and stability are the most frequently investigated properties in the market equilibrium models. On global and local markets we usually observe the lack of equilibrium. Nevertheless, the original model does not consider the possibility of stocks. However, we observe this situation, when there exists an excess supply. We should consider then how the accumulated stocks affect the equilibrium (or disequilibrium) and the stability of the model. During the seminar I will present the competitive economy model and the model with stocks. I will explore how these stocks influence the path of the price trajectory, equilibrium conditions and price stability.
15-04-2014 | Adam Nawrocki: Asymptotic behaviour of some \(/mu\)-almost periodic functions
The function \[ f(x)=\frac{1}{2+\cos{x}+\cos(x\sqrt{2})}\] is a classical example of an unbounded and continuous \(\mu\)-almost periodic function. For this function we have
\[\forall \varepsilon>0 \lim_{x \to \infty}x^{-2-\varepsilon}f(x)=0\]
During this lecture we will consider if changing the number \(\sqrt{2}\) to another irrational number may have relevant impact on the behaviour of this function. We shall construct such a number \(/alpha\)that the limit\[ \lim_{x \to \infty}x^{-2}f(x)=0\] will not exist.
The lecture will be preceded by a short speech by Marcin Borkowski.
01-04-2014 | dr Michał Goliński: About some properties of the space of almost periodic functions
We will be talking about some properties of the space \(AP(\mathbb R)\) of the almost periodic functions, in particular the properties of the weak topology on this space (Cauchy sequences, completeness, reflexivity).
25-03-2014 | Monika Naskręcka: Mathematical model of a competitive market with stocks.
Equilibrium and stability are the most frequently investigated properties in the market equilibrium models. On global and local markets we usually observe the lack of equilibrium. Nevertheless, the original model does not consider the possibility of stocks. However, we observe this situation, when there exists an excess supply. We should consider then how the accumulated stocks affect the equilibrium (or disequilibrium) and the stability of the model. During the seminar I will present the competitive economy model and the model with stocks. I will explore how these stocks influence the path of the price trajectory, equilibrium conditions and price stability.
18-03-2014 | Marcin Borkowski: On some application of Mönch theorem.
11-03-2014 | Dr Jacek Gulgowski (Institute of Mathematics, Gdańsk University): On the continuity of superposition operator in the spaces of functions of bounded variation
It is a well-know fact that the superposition of a function \(f\colon \mathbb R \to \mathbb R\) satisfying a local Lipschitz condition with a function \(x(t)\) of bounded variation leads to the function \((f\circ x)(t)\) which is also of bounded variation. During the seminar we are going to present a few results concerning the continuity of such a superposition operator \(F\colon BV[0,1]\to BV[0,1]\). Furthermore, we are going to discuss several generalizations of the concept of bounded variation in the sense of Jordan and investigate the issue of continuity of the superposition operator \(F\colon BV[0,1]\to E\), where \(E\) denotes the space of functions of bounded variation in the generalized sense.
04-03-2014 | Marcin Borkowski: On some application of Mönch theorem.
25-02-2014 | Marcin Borkowski: On some application of Mönch theorem.
28-01-2014 | Marcin Karczewski: Boltzmann kinetic equation
The aim of the seminar is to discuss the Boltzmann kinetic equation and its physical consequences. After gaining intuition we shall return to the earlier discussed VHP gas model.
28-01-2014 | Monika Naskręcka: Mathematical model of a competitive market with stocks.
Equilibrium and stability are the most frequently investigated properties in the market equilibrium models. On global and local markets we usually observe the lack of equilibrium. Nevertheless, the original model does not consider the possibility of stocks. However, we observe this situation, when there exists an excess supply. We should consider then how the accumulated stocks affect the equilibrium (or disequilibrium) and the stability of the model. During the seminar I will present the competitive economy model and the model with stocks. I will explore how these stocks influence the path of the price trajectory, equilibrium conditions and price stability.
21-01-2014 | Monika Naskręcka: Mathematical model of a competitive market with stocks.
Equilibrium and stability are the most frequently investigated properties in the market equilibrium models. On global and local markets we usually observe the lack of equilibrium. Nevertheless, the original model does not consider the possibility of stocks. However, we observe this situation, when there exists an excess supply. We should consider then how the accumulated stocks affect the equilibrium (or disequilibrium) and the stability of the model. During the seminar I will present the competitive economy model and the model with stocks. I will explore how these stocks influence the path of the price trajectory, equilibrium conditions and price stability.
14-01-2014 | prof. UW dr hab. Urszula Foryś (Warsaw University): Modelling of biochemical reactions with delays
Nowadays, in the description of biochemical reactions not only ordinary differential equations but also equations with delays are applied. Time delays can be used to reflect different time scales at which modelled reactions occur. During our (together with M. Bodnarem, J. Miękisz and J. Poleszczuk) research we have found that simple, intuitive methods of introducing delay can lead to improper conclusions, such as oscillatory dynamics of the simple protein delayed degradation process. I shall show that the simplest model proposed by Bartsun et al. (2005) should be modified. It occurs that to obtain oscillatory dynamics one needs to consider much more complex reactions channel, with negative feedback and dimerization.
07-01-2014 | dr Aneta Sikorska-Nowak: Nonlinear Sturm – Liouville dynamic equation
Will be presented the necessary concepts of dynamic equations on time scales, and nonlinear dynamic equation of Sturm-Liouville.
17-12-2013 | Marcin Karczewski: Boltzmann kinetic equation
The aim of the seminar is to discuss the Boltzmann kinetic equation and its physical consequences. After gaining intuition we shall return to the earlier discussed VHP gas model.
10-12-2013 | Marcin Karczewski: Boltzmann kinetic equation
The aim of the seminar is to discuss the Boltzmann kinetic equation and its physical consequences. After gaining intuition we shall return to the earlier discussed VHP gas model.
03-12-2013 | Piotr Kasprzak: Application of formal power series to differential equations
During the seminar we are going to discuss the Frobenius Method, that is, we are going to seek solutions to certain differential equations (not necessarily of integer-order) in the form of formal power (or Laurent) series. Several illustrative examples will be provided.
26-11-2013 | dr Aneta Sikorska-Nowak: Asymptotic stability of the integro-differential equation with delay
Certainly, the Lyapunov direct method has been, for more than 100 years, the main tool for the study of stability properties of ordinary, functional, integro-differential and partial differential equations. Nevertheless, the applications of this method to problem of stability in differential equations with delay has encountered serious difficulties if the delay is unbounded or if the equation has unbounded terms. The fixed point theory does not only solve the problem on stability but has a significant advantage over Lyapunov’s direct method.
I will present the results on the asymptotic stability of solutions of nonlinear integro-differential equations with delay using Sadovskii Fixed Point Theorem and properties of the measure of noncompactness.
19-11-2013 | dr Aneta Sikorska-Nowak: Asymptotic stability of the integro-differential equation with delay
Certainly, the Lyapunov direct method has been, for more than 100 years, the main tool for the study of stability properties of ordinary, functional, integro-differential and partial differential equations. Nevertheless, the applications of this method to problem of stability in differential equations with delay has encountered serious difficulties if the delay is unbounded or if the equation has unbounded terms. The fixed point theory does not only solve the problem on stability but has a significant advantage over Lyapunov’s direct method.
I will present the results on the asymptotic stability of solutions of nonlinear integro-differential equations with delay using Sadovskii Fixed Point Theorem and properties of the measure of noncompactness.
05-11-2013 | Monika Naskręcka: Mathematical model of a competitive market with stocks.
Equilibrium and stability are the most frequently investigated properties in the market equilibrium models. On global and local markets we usually observe the lack of equilibrium. Nevertheless, the original model does not consider the possibility of stocks. However, we observe this situation, when there exists an excess supply. We should consider then how the accumulated stocks affect the equilibrium (or disequilibrium) and the stability of the model. During the seminar I will present the competitive economy model and the model with stocks. I will explore how these stocks influence the path of the price trajectory, equilibrium conditions and price stability.
29-10-2013 | Monika Naskręcka: Mathematical model of a competitive market with stocks.
Equilibrium and stability are the most frequently investigated properties in the market equilibrium models. On global and local markets we usually observe the lack of equilibrium. Nevertheless, the original model does not consider the possibility of stocks. However, we observe this situation, when there exists an excess supply. We should consider then how the accumulated stocks affect the equilibrium (or disequilibrium) and the stability of the model. During the seminar I will present the competitive economy model and the model with stocks. I will explore how these stocks influence the path of the price trajectory, equilibrium conditions and price stability.
14-05-2013 | Piotr Kasprzak: Application of formal power series to differential equations
During the seminar we are going to discuss the Frobenius Method, that is, we are going to seek solutions to certain differential equations (not necessarily of integer-order) in the form of formal power (or Laurent) series. Several illustrative examples will be provided.
07-05-2013 | Piotr Kasprzak: Application of formal power series to differential equations
During the seminar we are going to discuss the Frobenius Method, that is, we are going to seek solutions to certain differential equations (not necessarily of integer-order) in the form of formal power (or Laurent) series. Several illustrative examples will be provided.
23-04-2013 | Dr hab. Aleksander Ćwiszewski: TITLE soon
09-04-2013 | Prof. dr hab. Bronisław Jakubczyk: Series of formally noncommutative variables versus functions and vector fields on manifolds
Taylor coefficients of a function can be calculated as iterated derivatives along constant vector fields (versors), computed at a fixed point. If a constant vector fields is replaced by any fixed set of vector fields on a manifold, a similar operation leads to the definition of a formal series with noncommutative variables.
We will show some interesting facts connected with such series, in particular the so-called realization theorem and its consequences. In particular, we will prove that a controlled and observed dynamical system on a manifold can be represented by such a series. Another consequence is a new test of convergence of a series of noncommutative variables.
05-03-2013 | Jędrzej Sadowski: About integrate-and-fire models
We will talk about two integrate-and-fire models.
The first one will be the neon bulb circuit, the second a japanese water toy.
26-02-2013 | Piotr Zdanowicz: Basic properties of formal series
During the seminar we will discuss and prove some properties of formal series.
19-02-2013 | Marcin Borkowski: Some properties of the Henstock-Kurzweil Integral
During this seminar we will discuss some properties of the Henstock-Kurzweil Integral for an unbounded domain. In particular we shall prove that the functions of significantly bounded variation are multipliers of HK-integrable functions.
22-01-2013 | Marcin Borkowski: Some properties of the Henstock-Kurzweil Integral
During this seminar we will discuss some properties of the Henstock-Kurzweil Integral for an unbounded domain. In particular we shall prove that the functions of significantly bounded variation are multipliers of HK-integrable functions.
15-01-2013 | Marcin Borkowski: Some properties of the Henstock-Kurzweil Integral
During this seminar we will discuss some properties of the Henstock-Kurzweil Integral for an unbounded domain. In particular we shall prove that the functions of significantly bounded variation are multipliers of HK-integrable functions.
08-01-2013 | Monika Naskręcka: Homeomorphism of the space of polynomials and the space of their roots
During this seminar an elementary, topological proof of continuity of the roots of complex polynomials with respect to their roots will be shown. For normed polynomials with complex coefficients and properly defined metric spaces this theorem can be expressed as a homeomorphism of corresponding metric spaces of coeffecients and roots.
18-12-2012 | Monika Naskręcka: Homeomorphism of the space of polynomials and the space of their roots
During this seminar an elementary, topological proof of continuity of the roots of complex polynomials with respect to their roots will be shown. For normed polynomials with complex coefficients and properly defined metric spaces this theorem can be expressed as a homeomorphism of corresponding metric spaces of coeffecients and roots.
11-12-2012 | Monika Naskręcka: Homeomorphism of the space of polynomials and the space of their roots
During this seminar an elementary, topological proof of continuity of the roots of complex polynomials with respect to their roots will be shown. For normed polynomials with complex coefficients and properly defined metric spaces this theorem can be expressed as a homeomorphism of corresponding metric spaces of coeffecients and roots.
04-12-2012 | Piotr Maćkowiak: The existence of surplus demand function zeros
27-11-2012 | Piotr Zdanowicz: Basic properties of formal series
During the seminar we will discuss and prove some properties of formal series.
20-11-2012 | Piotr Zdanowicz: Basic properties of formal series
During the seminar we will discuss and prove some properties of formal series.
13-11-2012 | Piotr Kasprzak: On a certain class of functions of \(\Lambda\)-bounded variation
During the seminar we are going to define a certain class of functions of \(\Lambda\)-bounded variation and prove some properties of such functions. Furthermore, we are going to show that endowed with a certain functional the class in questions becomes a strictly convex Banach space. We are also going to provide several non-trivial examples illustrating our considerations.
06-11-2012 | Justyna Signerska: Firing map for integrate-and-fire models with an almost periodic drive
Consider the integrate-and-fire system \(\dot{x}=F(t,x)\), \(F \colon \mathbb R \to \mathbb R\), in which the continuous dynamics is interrupted by the threshold-and-reset behaviour: \(\lim_{t \to s^+}x(t)=x_r\) if \(x(s)=x_{\Theta}\), meaning that once the value of a dynamical variable \(x(t)\) reaches a certain threshold \(x=x_{Theta}\) it is immediately reset to a resting value \(x_r\) and the system evolves again according to the differential equation. The question is to describe the time series of consecutive resets (spikes) \(t_n\) as iterations \(\Phi^n(t_0)\) of some map \(\Phi\colon \mathbb R \to \mathbb R\), called the firing map, and the sequence of interspike-intervals \(t_n – t_{n-1}\) as a sequence of displacements \(\Phi^n(t_0)-\Phi^{n-1}(t_0)\) along a trajectory of this map. The problem appears in various applications, e.g. in modelling of an action potential (spiking) by a neuron.
However, so far properties of the firing map were analytically investigated only for the function \(F\), which is smooth enough and often also periodic in \(t\). We present a complete description of the properties of the firing map arising from the most popular models: \(\dot{x}=-\sigma x +f(t)\) (Leaky Integrate-and-Fire) and \(\dot{x}=f(t)\) (Perfect Integrator), when the function \(f\) is only locally integrable and/or almost periodic. In particular, we prove that a Stepanov almost periodic function \(f\) induces the firing map \(\Phi\) with the uniformly (Bohr) almost periodic displacement \(\Phi-Id\). In this way we provide a formal framework for next studying of the interspike-intervals in almost-periodically driven integrate-and-fire models.
30-10-2012 | Piotr Kasprzak: On a certain class of functions of \(\Lambda\)-bounded variation
During the seminar we are going to define a certain class of functions of \(\Lambda\)-bounded variation and prove some properties of such functions. Furthermore, we are going to show that endowed with a certain functional the class in questions becomes a strictly convex Banach space. We are also going to provide several non-trivial examples illustrating our considerations.
23-10-2012 | Piotr Kasprzak: On a certain class of functions of \(\Lambda\)-bounded variation
During the seminar we are going to define a certain class of functions of \(\Lambda\)-bounded variation and prove some properties of such functions. Furthermore, we are going to show that endowed with a certain functional the class in questions becomes a strictly convex Banach space. We are also going to provide several non-trivial examples illustrating our considerations.
16-10-2012 | Piotr Maćkowiak: The existence of surplus demand function zeros
09-10-2012 | Piotr Maćkowiak: The existence of surplus demand function zeros
29-05-2012 | Piotr Kasprzak: On a certain class of functions of bounded variation
We are going to define a relatively large class of functions of bounded variation defined on an open subset of \(\mathbb R^n\), which in particular contains the Sobolev space \(W^{1,1}(\Omega)\). Furthermore, we are going to discuss the connection between the classical variation in the sense of Jordan and the generalized one.
22-05-2012 | Michał Burzyński: Alternative proofs of Arrow’s impossibility theorem
Arrow’s impossibility theorem states, that if there are at least three potential social states, there is no such social welfare function \(f\) (that describes the society as a whole with given individual preferences), which satisfies the following four conditions: \(f\) has an unbounded domain; the strong relation of social preferences satisfies the weak Pareto principle; \(f\) satisfies the property of independence of irrelevant alternatives and in a society with preferences described with the function \(f\) there is no dictatorship. The original proof, given by K. Arrow, consists of two steps: to show the existence of a deciding unit and to prove, it must be a dictator. The first of the alternative proofs is based on using the Condorcet preference. The second proof applies the first step of Arrow’s proof and points, that all social decisions are made in the same way. The last proof is of graphic character.
15-05-2012 | Michał Burzyński: Alternative proofs of Arrow’s impossibility theorem
Arrow’s impossibility theorem states, that if there are at least three potential social states, there is no such social welfare function \(f\) (that describes the society as a whole with given individual preferences), which satisfies the following four conditions: \(f\) has an unbounded domain; the strong relation of social preferences satisfies the weak Pareto principle; \(f\) satisfies the property of independence of irrelevant alternatives and in a society with preferences described with the function \(f\) there is no dictatorship. The original proof, given by K. Arrow, consists of two steps: to show the existence of a deciding unit and to prove, it must be a dictator. The first of the alternative proofs is based on using the Condorcet preference. The second proof applies the first step of Arrow’s proof and points, that all social decisions are made in the same way. The last proof is of graphic character.
08-05-2012 | Michał Burzyński: Alternative proofs of Arrow’s impossibility theorem
Arrow’s impossibility theorem states, that if there are at least three potential social states, there is no such social welfare function \(f\) (that describes the society as a whole with given individual preferences), which satisfies the following four conditions: \(f\) has an unbounded domain; the strong relation of social preferences satisfies the weak Pareto principle; \(f\) satisfies the property of independence of irrelevant alternatives and in a society with preferences described with the function \(f\) there is no dictatorship. The original proof, given by K. Arrow, consists of two steps: to show the existence of a deciding unit and to prove, it must be a dictator. The first of the alternative proofs is based on using the Condorcet preference. The second proof applies the first step of Arrow’s proof and points, that all social decisions are made in the same way. The last proof is of graphic character.
24-04-2012 | Piotr Kasprzak: On a certain class of functions of bounded variation
We are going to define a relatively large class of functions of bounded variation defined on an open subset of \(\mathbb R^n\), which in particular contains the Sobolev space \(W^{1,1}(\Omega)\). Furthermore, we are going to discuss the connection between the classical variation in the sense of Jordan and the generalized one.
03-04-2012 | Piotr Kasprzak: On the compactness criterion in the space of bounded real-valued continuous functions defined on a non-compact domain
During the seminar we are going to discuss a certain compactness criterion in the space of bounded real-valued continuous functions defined on a non-compact domain related to the well-known Arzela-Ascoli theorem.
27-03-2012 | Piotr Maćkowiak: Exploding points
We will present and prove theorem of the exploding point. This theorem states that for any function defined on a compact set X, containing the cube K centered at zero in its interior, with values in X\K, which is the identity on the boundary of the set X, there exists a point c in X, that in any surroundings of c, there is a point x such that the value of f(x) and f(c) are located on opposite walls of the cube K.
20-03-2012 | Adam Nawrocki: An Application of Continued Fractions
During this seminar we will discuss basic properties of Continued Fractions. Next we shall use Continued Fractions to calculate the limit of:\[ \lim_{x \to \infty} \frac{e^{-x}}{2+\cos(x) + \cos(x\sqrt{2})}.\]
13-03-2012 | Adam Nawrocki: An Application of Continued Fractions
During this seminar we will discuss basic properties of Continued Fractions. Next we shall use Continued Fractions to calculate the limit of:\[ \lim_{x \to \infty} \frac{e^{-x}}{2+\cos(x) + \cos(x\sqrt{2})}.\]
06-03-2012 | Marcin Wachowiak: Applications of Theorem Hopf-Lefschetz fixed point
In the first part of the discussion we introduce the necessary concepts and facts about the homology and cohomology, then we will discuss the Hopf-Lefschetz theorem and its applications
28-02-2012 | Jędrzej Sadowski: Definitions of the N-almost periodic functions
We will show differend ways to define N-almost periodic functions and prove their equivalence.
21-02-2012 | Jędrzej Sadowski: Definitions of the N-almost periodic functions
We will show differend ways to define N-almost periodic functions and prove their equivalence.
14-02-2012 | Jędrzej Sadowski: Definitions of the N-almost periodic functions
We will show differend ways to define N-almost periodic functions and prove their equivalence.
24-01-2012 | Daria Bugajewska: On differential and inetgral equations in the spaces of functions of Lambda-bounded variation.
We are going to consider linear differential and nonlinear integral equations in the
spaces of functions of Lambda-bounded variation. We will state the existence and the existence and uniqueness results in this space as well as in its subspace consisting of contninuous functions of Lambda-bounded variation.
17-01-2012 | Daria Bugajewska: On differential and inetgral equations in the spaces of functions of Lambda-bounded variation.
We are going to consider linear differential and nonlinear integral equations in the
spaces of functions of Lambda-bounded variation. We will state the existence and the existence and uniqueness results in this space as well as in its subspace consisting of contninuous functions of Lambda-bounded variation.
10-01-2012 | Daria Bugajewska: On differential and inetgral equations in the spaces of functions of Lambda-bounded variation.
We are going to consider linear differential and nonlinear integral equations in the
spaces of functions of Lambda-bounded variation. We will state the existence and the existence and uniqueness results in this space as well as in its subspace consisting of contninuous functions of Lambda-bounded variation.
03-01-2012 | Jędrzej Sadowski: Definitions of the N-almost periodic functions
We will show differend ways to define N-almost periodic functions and prove their equivalence.
20-12-2011 | Jędrzej Sadowski: Definitions of the N-almost periodic functions
We will show differend ways to define N-almost periodic functions and prove their equivalence.
13-12-2011 | Marcin Wachowiak: Applications of Theorem Hopf-Lefschetz fixed point
In the first part of the discussion we introduce the necessary concepts and facts about the homology and cohomology, then we will discuss the Hopf-Lefschetz theorem and its applications
06-12-2011 | Marcin Wachowiak: Applications of Theorem Hopf-Lefschetz fixed point
In the first part of the discussion we introduce the necessary concepts and facts about the homology and cohomology, then we will discuss the Hopf-Lefschetz theorem and its applications
29-11-2011 | Marcin Wachowiak: Applications of Theorem Hopf-Lefschetz fixed point
In the first part of the discussion we introduce the necessary concepts and facts about the homology and cohomology, then we will discuss the Hopf-Lefschetz theorem and its applications
22-11-2011 | Marcin Wachowiak: Applications of Theorem Hopf-Lefschetz fixed point
In the first part of the discussion we introduce the necessary concepts and facts about the homology and cohomology, then we will discuss the Hopf-Lefschetz theorem and its applications
15-11-2011 | Marcin Borkowski, Piotr Maćkowiak (Poznań University of Economics): On superposition of formal power series
We will present a new proof of a criterion for existence of superposition of formal power series given by Gan and Knox. We will also give some properties concerning the behavior of such series on the boundary of their convergence circle.
08-11-2011 | Marcin Borkowski, Piotr Maćkowiak (Poznań University of Economics): On superposition of formal power series
We will present a new proof of a criterion for existence of superposition of formal power series given by Gan and Knox. We will also give some properties concerning the behavior of such series on the boundary of their convergence circle.
25-10-2011 | Adam Burchard: Schauder fixed point, revisited
During the seminar we are going to discuss the following generalization of the classical Schauder fixed point theorem due to R. Cauty:
Let \(C\) be a convex subset of a topological vector space \(E\). If \(f\colon C \to C\) is a continuous function such that \(f(C)\) is contained in a compact subset of \(C\), then \(f\) has a fixed point.
The talk is based on the following paper: R. Cauty, Solution du problème de point fixe de Schauder, Fund. Math. 170 (2001), 231-246.
18-10-2011 | Adam Burchard: Schauder fixed point, revisited
During the seminar we are going to discuss the following generalization of the classical Schauder fixed point theorem due to R. Cauty:
Let \(C\) be a convex subset of a topological vector space \(E\). If \(f\colon C \to C\) is a continuous function such that \(f(C)\) is contained in a compact subset of \(C\), then \(f\) has a fixed point.
The talk is based on the following paper: R. Cauty, Solution du problème de point fixe de Schauder, Fund. Math. 170 (2001), 231-246.
11-10-2011 | Adam Burchard: Schauder fixed point, revisited
During the seminar we are going to discuss the following generalization of the classical Schauder fixed point theorem due to R. Cauty:
Let \(C\) be a convex subset of a topological vector space \(E\). If \(f\colon C \to C\) is a continuous function such that \(f(C)\) is contained in a compact subset of \(C\), then \(f\) has a fixed point.
The talk is based on the following paper: R. Cauty, Solution du problème de point fixe de Schauder, Fund. Math. 170 (2001), 231-246.
04-10-2011 | Adam Burchard: Schauder fixed point, revisited
During the seminar we are going to discuss the following generalization of the classical Schauder fixed point theorem due to R. Cauty:
Let \(C\) be a convex subset of a topological vector space \(E\). If \(f\colon C \to C\) is a continuous function such that \(f(C)\) is contained in a compact subset of \(C\), then \(f\) has a fixed point.
The talk is based on the following paper: R. Cauty, Solution du problème de point fixe de Schauder, Fund. Math. 170 (2001), 231-246.
14-06-2011 | Marcin Borkowski: Some remarks on convergence of power series at the boundary of the convergence circle
We will present a theorem concerning convergence of power series—together with all its derivatives—at the boundary of the convergence circle.
24-05-2011 | Joanna Wypych: On superposition of formal power series
In the beginning we will present basic definitions concerning formal power series and their properties. Then we will discuss two theorems on superposition of such series. The talk is based on a paper On composition of formal power series by Xiao-Xiong Gan and Nathaniel Knox.
17-05-2011 | Joanna Wypych: On superposition of formal power series
In the beginning we will present basic definitions concerning formal power series and their properties. Then we will discuss two theorems on superposition of such series. The talk is based on a paper On composition of formal power series by Xiao-Xiong Gan and Nathaniel Knox.
10-05-2011 | Joanna Wypych: On superposition of formal power series
In the beginning we will present basic definitions concerning formal power series and their properties. Then we will discuss two theorems on superposition of such series. The talk is based on a paper On composition of formal power series by Xiao-Xiong Gan and Nathaniel Knox.
19-04-2011 | Piotr Kasprzak: On the equivalent characterizations of Levitan almost periodic functions
12-04-2011 | Marcin Borkowski: On formal power series
The aim of the talk is to give an introduction into the theory of formal power series. After the basic definitions and properties we will show some application to combinatorics. Finally, we will show an example of a formal differential equation.
05-04-2011 | Adam Nawrocki: Examples of Henstock-Kurzweil integrable functions
We will present methods of proving Henstock-Kurzweil integrability of real functions.
29-03-2011 | Piotr Kasprzak: On a new class of almost periodic functions
During the talk not only will we define the so-called quasi almost automorphic functions but also we will prove some basic properties of these functions.
22-03-2011 | Joanna Wypych: Formal power series
We will discuss basic properties of formal power series and the Krull topology. Among others, we will present theorems on the distributive laws and invertibility of a series. The talk will be based on the book by S. Łojasiewicz and J. Stasica Formal analysis and analytic functions (in Polish).
15-03-2011 | Marcin Borkowski: On formal power series
The aim of the talk is to give an introduction into the theory of formal power series. After the basic definitions and properties we will show some application to combinatorics. Finally, we will show an example of a formal differential equation.
08-03-2011 | Joanna Wypych: Formal power series
We will discuss basic properties of formal power series and the Krull topology. Among others, we will present theorems on the distributive laws and invertibility of a series. The talk will be based on the book by S. Łojasiewicz and J. Stasica Formal analysis and analytic functions (in Polish).
01-03-2011 | Marcin Borkowski: On the dual space to the space of Henstock-Kurzweil integrable functions
During the talk we will present the result of Alexiewicz which gives a characterization of the dual space to the space of Henstock-Kurzweil integrable functions defined on a bounded interval.
22-02-2011 | Piotr Kasprzak: On the equivalent characterizations of Levitan almost periodic functions
18-01-2011 | Joanna Wypych: Formal power series
We will discuss basic properties of formal power series and the Krull topology. Among others, we will present theorems on the distributive laws and invertibility of a series. The talk will be based on the book by S. Łojasiewicz and J. Stasica Formal analysis and analytic functions (in Polish).
11-01-2011 | Marcin Wachowiak: A fixed point theorem for mappings satisfying the interior condition
In this talk, we will prove a fixed point theorem for condensing mappings satisfying a new Leray-Schauder type condition proposed by Antonio Jimenez-Melado and Claudio H. Morales, the so-called interior condition. We will also show some examples, proving that this condition is in general independent of the classical Leray-Schauder boundary condition. Finally, we will prove that for nonexpansive mappings of Hilbert spaces, the interior condition implies the Leray-Schauder condition.
04-01-2011 | Wojciech Jankowski: On a certain fixed point theorem for discontinuous mappings
21-12-2010 | Marcin Borkowski: On formal power series
The aim of the talk is to give an introduction into the theory of formal power series. After the basic definitions and properties we will show some application to combinatorics. Finally, we will show an example of a formal differential equation.
14-12-2010 | Piotr Kasprzak: On the compactness criterion in the space of bounded real-valued continuous functions defined on a non-compact domain
07-12-2010 | Marcin Wachowiak: A fixed point theorem for mappings satisfying the interior condition
In this talk, we will prove a fixed point theorem for condensing mappings satisfying a new Leray-Schauder type condition proposed by Antonio Jimenez-Melado and Claudio H. Morales, the so-called interior condition. We will also show some examples, proving that this condition is in general independent of the classical Leray-Schauder boundary condition. Finally, we will prove that for nonexpansive mappings of Hilbert spaces, the interior condition implies the Leray-Schauder condition.
30-11-2010 | Marcin Wachowiak: A fixed point theorem for mappings satisfying the interior condition
In this talk, we will prove a fixed point theorem for condensing mappings satisfying a new Leray-Schauder type condition proposed by Antonio Jimenez-Melado and Claudio H. Morales, the so-called interior condition. We will also show some examples, proving that this condition is in general independent of the classical Leray-Schauder boundary condition. Finally, we will prove that for nonexpansive mappings of Hilbert spaces, the interior condition implies the Leray-Schauder condition.
23-11-2010 | Marcin Wachowiak: A fixed point theorem for mappings satisfying the interior condition
In this talk, we will prove a fixed point theorem for condensing mappings satisfying a new Leray-Schauder type condition proposed by Antonio Jimenez-Melado and Claudio H. Morales, the so-called interior condition. We will also show some examples, proving that this condition is in general independent of the classical Leray-Schauder boundary condition. Finally, we will prove that for nonexpansive mappings of Hilbert spaces, the interior condition implies the Leray-Schauder condition.
16-11-2010 | Marcin Borkowski: O pewnych problemach związanych ze splotem funkcji, cz. 3
Splot funkcji całkowalnych w sensie Lebesgue’a jest klasycznym pojęciem, którego przeniesienie na grunt teorii całek nieabsolutnie zbieżnych napotyka na zaskakujące trudności. W referacie przedstawimy niektóre z tych problemów oraz przedstawimy kontrprzykłady pokazujące, że splot zdefiniowany przy użyciu całki Henstocka-Kurzweila nie ma własności analogicznych do przypadku \(L^1\).
09-11-2010 | Marcin Borkowski: O pewnych problemach związanych ze splotem funkcji, cz. 2
Splot funkcji całkowalnych w sensie Lebesgue’a jest klasycznym pojęciem, którego przeniesienie na grunt teorii całek nieabsolutnie zbieżnych napotyka na zaskakujące trudności. W referacie przedstawimy niektóre z tych problemów oraz przedstawimy kontrprzykłady pokazujące, że splot zdefiniowany przy użyciu całki Henstocka-Kurzweila nie ma własności analogicznych do przypadku \(L^1\).
26-10-2010 | Marcin Borkowski: O pewnych problemach związanych ze splotem funkcji, cz. 1
Splot funkcji całkowalnych w sensie Lebesgue’a jest klasycznym pojęciem, którego przeniesienie na grunt teorii całek nieabsolutnie zbieżnych napotyka na zaskakujące trudności. W referacie przedstawimy niektóre z tych problemów oraz przedstawimy kontrprzykłady pokazujące, że splot zdefiniowany przy użyciu całki Henstocka-Kurzweila nie ma własności analogicznych do przypadku \(L^1\).
